AbstractPurposeThe diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy (TBB) using radial probe endobronchial ultrasound (RP-EBUS) is 71%, which is lower than that of transthoracic needle biopsy. We investigated the performance and safety of sequential transbronchial cryobiopsy (TBC) using a novel 1.1-mm diameter cryoprobe, after conventional TBB using RP-EBUS for the diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions (PLLs).
Materials and MethodsFrom April 2021 to November 2021, 110 patients who underwent bronchoscopy using RP-EBUS for the diagnosis of PLL ≤ 30 mm were retrospectively included in our study. All records were followed until June 2022.
ResultsThe overall diagnostic yield of combined TBB and TBC was 79.1%, which was higher than 60.9% of TBB alone (p=0.005). The diagnostic yield of sequential TBC was 65.5%, which increased the overall diagnostic yield by 18.2%. The surface area of tissues by TBC (mean area, 18.5 mm2) was significantly larger than those of TBB by 1.5-mm forceps (3.4 mm2, p < 0.001) and 1.9-mm forceps (3.7 mm2, p=0.011). In the multivariate analysis, PLLs with the longest diameter of ≤ 22 mm were found to be related to additional diagnostic benefits from sequential TBC (odds ratio, 3.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.043 to 11.775; p=0.042). Complications were found in 10.5% of the patients: pneumothorax (1.0%), infection (1.0%), and significant bleeding (8.6%). None of the patients developed any life-threatening complications.
IntroductionSince the introduction of the National Lung Screening Trial, low-dose computed tomography (CT) screening for early detection of lung cancer has become a standard in high-risk populations [1]. Although it contributed to reducing lung cancer mortality, most peripheral lung lesions (PLLs) were finally diagnosed as benign [2]. Identifying whether a PLL is malignant or benign is becoming increasingly important for pulmonary physicians to avoid unnecessary invasive procedures [3].
Radial probe endobronchial ultrasound (RP-EBUS) has been traditionally used for the detection of PLLs during bronchoscopy [4]. A major advantage is that PLLs can be sampled more safely using ancillary tools such as guide sheath (GS), as opposed to transthoracic needle biopsy [5,6]. However, a recent meta-analysis reported that the pooled diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy (TBB) using RP-EBUS for PLLs is about 71%, which is much lower than that of transthoracic needle biopsy [7].
The combination of RP-EBUS and transbronchial cryobiopsy (TBC) for PLLs is considered one of the alternatives to improve the performance of conventional TBB using RP-EBUS [8–10]. A recent study regarding the additional TBC using a 1.9-mm diameter cryoprobe after forceps biopsy demonstrated promising results [11]. However, it is difficult to insert a 1.9-mm diameter cryoprobe through a 2.0-mm channel of a thin bronchoscope, especially in both upper lobes which require large bending angle of the bronchoscope (S1 Fig.). Recently, a novel 1.1-mm diameter cryoprobe was introduced for the diagnosis of PLL, which has little evidence so far. We investigated the performance and safety of sequential TBC using a 1.1-mm cryoprobe, which was performed after conventional TBB using RP-EBUS for the diagnosis of PLLs.
Materials and Methods1. Study populationThis retrospective cohort study was performed from April 2021 to November 2021 using the bronchoscopy registry of Pusan National University Hospital, a tertiary referral hospital in Busan, South Korea. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients aged ≥ 18 years, (2) patients with PLL ≤ 30 mm, and (3) patients who underwent bronchoscopy using RP-EBUS. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients who received additional procedures, including convex probe EBUS, (2) patients who underwent bronchoscopic re-biopsy for mutation analyses [12], or (3) patients with visually inspectable endobronchial lesion. PLL was defined as an abnormal pulmonary opacity beyond the segmental bronchus on a CT scan [13]. This study was approved by the institutional review board of the Pusan National University Hospital (IRB No. 2112-027-110). The medical records of all study subjects were followed up until June 2022.
2. Bronchoscopy procedures
S2 Fig. shows a representative case. After conscious sedation with intravenous midazolam and fentanyl, oropharyngeal intubation was performed using an 8.0-mm inner diameter endotracheal tube under the guidance of a 4.0-mm diameter thin bronchoscope (BF-P260F, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). After inspection of the tracheobronchial tree, a thin bronchoscope was introduced close to the target PLL under the guidance of the CT image [14] and virtual bronchoscopic navigation (LungPoint, Broncus Medical, Mountain View, CA) [15,16]. To localize the target PLL, RP-EBUS (UM-S20-17S, Olympus) combined with GS (K-201, Olympus) was inserted. If not detected, a 3.0-mm diameter ultrathin bronchoscope (BF-MP190F, Olympus) was inserted using RP-EBUS without GS. When the PLL was identified, TBB using 1.5-mm forceps (FB-233D, Olympus) and/or transbronchial needle aspiration using a dedicated needle (PeriView FLEX, NA-403D-2021, Olympus) was performed under X-ray fluoroscopic guidance. If adequate tissue was not collected, at the discretion of the investigator, 1.9-mm forceps were used after removing the GS via a thin bronchoscope. After the initial TBB, the location of the target PLL was identified again using RP-EBUS with or without GS followed by a 1.1 mm cryoprobe insertion. The freezing time was determined at the discretion of the pulmonologist (range, 6 to 8 seconds). After freezing the target lesion, the bronchoscope and a 1.1-mm cryoprobe with the specimen were removed en bloc, and frozen specimens were thawed in normal saline at room temperature. Thereafter, the bronchoscope was immediately reinserted into the bronchial tree to determine the severity of bleeding at the biopsy site. When bleeding was uncontrolled with a thin or ultrathin bronchoscope, a therapeutic bronchoscope with a larger channel size (BF-1T260 or BF-1TQ290, Olympus) was inserted to secure a clear view from substantial bleeding. Additionally, a balloon catheter (B5-2C, Olympus) was used to control bleeding at the pulmonologist’s discretion. Samples of conventional TBB and TBC were fixed in different tubes of 10% formalin solution, and histological diagnoses were separately evaluated by the same pathologists.
Chest radiographs were obtained 2–4 hours after bronchoscopy to check for iatrogenic pneumothorax. After the procedure, oral prophylactic antibiotics were prescribed for 3–5 days to prevent infectious complications.
3. DiagnosisThe presence of atypical cells, non-specific inflammation, or suspicious findings in histological reports were regarded as inconclusive, which led to one of the following clinical decisions: surgical biopsy, repeated bronchoscopy, transthoracic needle biopsy or clinical follow-up with a CT scan every 3–6 months.
Benign disease, not otherwise specified, was defined as follows: (1) ≥ 30% reduction in the mean size of the lung lesion (average of the longest diameter and perpendicular diameter on axial CT image), or (2) no change or < 30% reduction in the mean size during a follow-up period of at least 12 months (last follow-up, 30 June 2022). The final diagnoses were determined based on the histological results, microbiological studies, or clinical follow-up.
4. Variables and outcomesBefore the procedure, radiological variables were analyzed as follows: the level of bronchus on the CT scan, the presence of bronchus sign, the morphological category of lung nodule, the longest and mean diameters of the target lesion, the distance from the visceral pleura to the target lesion, and the lobar location of the target lesion. During the procedure, the following variables were recorded: procedure duration from the insertion of the bronchoscope into the mouth to removal from the mouth, ultrasonographic findings of the target lesion [4,17], freezing time of crybiopsy, and bleeding with its management after biopsy. After the procedure, procedure-related complications such as pneumothorax, infection, respiratory failure, and other unexpected complications were also recorded in electronic medical records.
The primary outcomes of the present study were the overall histopathological diagnostic yield (combined TBB and TBC) and the additional yield of TBC. The secondary outcome was the tissue surface area, calculated by multiplying the longest diameter by its vertical diameter using the largest tissue sample in each bronchoscopy procedure. Diagnostic yield was calculated as the number of procedures with a successful diagnosis divided by the total number of procedures.
5. Statistical analysisContinuous and categorical variables in the study results are presented as mean (range) and number (percentage), respectively. Pearson’s chi-square or Fisher exact test was used to compare categorical variables. In addition, continuous variables were compared using the independent t test, paired t test, or Wilcoxon signed-rank test according to the normality test. The diagnostic yield between the combined procedures (TBB and TBC) and the conventional TBB was compared using the two-proportion test. Using variables with a p-value < 0.2 in univariate analyses or known important characteristics, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the factors with diagnostic benefits from sequential TBC. p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant and R software for Windows (ver. 4.1.3, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) was used for statistical analyses.
Results1. Study populationDuring the study period, 125 patients with PLL ≤ 30 mm underwent bronchoscopy using RP-EBUS (Fig. 1). After excluding 15 patients, 110 patients who were scheduled for a combined procedure with conventional TBB using RP-EBUS and sequential TBC using a 1.1-mm cryoprobe were included in the study. The baseline characteristics of the study population are presented in Table 1. The mean lesion size in the longest diameter was 22 mm (range, 9 to 30 mm), and 42 patients (38.2%) had PLL ≤ 20 mm. The prevalence of malignancy was 83.6% and the final diagnoses of all the study patients are shown in Table 2.
2. Bronchoscopy procedures
Table 3 shows the results of the bronchoscopy procedures. Using RP-EBUS, ‘within’ and ‘adjacent to’ images were found in 82 (74.5%) and 23 patients (20.9%), respectively. Except for five patients (4.5%) with invisible lesions on RP-EBUS, 105 patients underwent sequential TBC after conventional TBB (S3 Table).
3. OutcomesThe overall histopathological diagnostic yield of the bronchoscopy procedure (co-primary outcome) was 79.1% (87 of 110), which was significantly higher than the 60.9% (67 of 110) yield of conventional TBB alone (p=0.005). The histopathological diagnostic yield of sequential TBC was 65.5% (72 of 110), and 20 patients (18.2%) were additionally diagnosed using sequential TBC (Fig. 2). Brush cytology and needle aspiration were both diagnostic in one case (one in nine for brushing cytology and one in six for needle aspiration), which did not contribute to the increase in the diagnostic yield of conventional TBB. Especially, there was no difference in the diagnostic yield of TBC between PLL with acute angle (the apical segment of right upper lobe and apicoposterior segment of left upper division) and the others (63.3% vs. 66.3%, p=0.774). Additional surgical biopsy, repeated bronchoscopy, transthoracic needle biopsy, and follow-up CT scan were performed in eight, three, one, and seven patients, respectively, in study subjects whose diagnosis was not confirmed by the bronchoscopy procedure (S4 Table).
The mean longest diameter of the tissue sample collected by sequential TBC was 5.3 mm (range, 2 to 26 mm), which was significantly longer than those of conventional TBB using 1.5-mm forceps (2.4 mm; range, 1 to 6; p < 0.001) and 1.9-mm forceps (2.5 mm; range, 1 to 4; p=0.014) (Fig. 3). In addition, there were significant differences in the mean surface area of the tissue between sequential TBC (18.5 mm2; range, 4 to 78) and both TBB using 1.5-mm forceps (3.4 mm2; range, 1 to 18; p < 0.001) and 1.9-mm forceps (3.7 mm2; range, 1 to 12; p=0.011).
4. Diagnostic benefits of cryobiopsyUnivariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to determine the factors related to the additional diagnostic benefit from sequential TBC (20 patients diagnosed with cryobiopsy only vs. 67 diagnosed irrespective of the cryobiopsy results) (Table 4). As a result, PLLs with the longest diameter of ≤ 22 mm were related to additional diagnostic benefits from sequential TBC in the multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 3.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.043 to 11.775; p=0.042).
5. Safety profileOf the 105 study patients who underwent sequential TBC, procedure-related complications were found in 11 patients (10.5%). Pneumothorax without chest tube insertion was identified in one patient (1.0%). Prophylactic antibiotics were prescribed to 104 study subjects (99.0%), and a procedure-related lung infection was found in one case (1.0%) without antibiotics. Uncontrolled bleeding with a thin or ultrathin bronchoscope was found in nine patients (8.6%); therapeutic bronchoscopy with a larger channel size was used in all patients, and hemostatic tamponade using a balloon catheter was performed in five patients (4.8%). None of the study patients developed life-threatening complications, including serious bleeding or mortality.
DiscussionThis is the first study to evaluate the additive impact of a 1.1 mm cryoprobe on conventional TBB using RP-EBUS. We found that the diagnostic yield of the combined procedure of conventional TBB and sequential TBC using RP-EBUS was 79.1% in patients with PLL ≤ 30 mm, which suggest that sequential TBC using a 1.1-mm cryoprobe is a potential method to improve the performance of TBB using RP-EBUS.
The cryobiopsy method, which uses the cryoadhesive effect (the Joule-Thomson effect) [18], can easily collect large amounts of appropriate tissue samples, and thus, can be used in bronchoscopy procedures for the diagnosis of PLL [8]. Previous meta-analysis showed that there was no difference in the pooled diagnostic yield between cryobiopsy and forceps biopsy for PLLs when combined with RP-EBUS (77.0% and 72.0%, respectively) [9], whereas, Matsumoto et al. [11] recently reported that the diagnostic yield of conventional TBB and sequential TBC using a 1.9-mm cryoprobe for PLLs (irrespective of lesion size) was found to be up to 89.9%. However, 1.9-mm cryoprobe is not flexible enough to advance to bronchi with an acute angle, such as both upper lobes. Therefore, the position of the RP-EBUS and the cryoprobe may be different on fluoroscopic images, which may confuse respiratory physicians in identifying the exact location of the target lesion. On the contrary, 1.1-mm cryoprobe is flexible enough to advance to the bronchi with an acute angle as seen in S1 Fig.; this could be a potent tool for the diagnosis of PLL. However, the issue concerning the affordability of performing TBC combined with RP-EBUS still exists, since RP-EBUS is not covered by the National Health Insurance in South Korea.
In the current study, 67 patients were successfully diagnosed without sequential TBC; whereas 20 patients were diagnosed using cryobiopsy samples only. In the multivariate analysis, PLLs with the longest diameter of ≤ 22 mm were identified as an independent factor with an additional diagnostic benefit from cryobiopsy. Previous studies have shown that the size of the PLL is significantly related to the diagnostic yield of bronchoscopy [19–22]; that is, the smaller the size, the lower the diagnosis rate. Our data suggest that sequential TBC is a reasonable method to increase the diagnostic yield of small PLL, especially those ≤ 22 mm. However, 15 patients were diagnosed using forceps samples only. This could be associated with potential bleeding, edema, and position change of lung nodules during TBB prior to TBC, but warrants further studies with larger cohorts for validation.
The overall complication rate of the bronchoscopy procedures was 10.5% in the study, which was higher than that of conventional TBB using RP-EBUS in previous studies (0%–7.4%) [23]. Most of which were uncontrolled bleeding using a thin or ultrathin bronchoscope after TBC (8.6%); however, all were adequately managed using a therapeutic bronchoscope with or without a balloon catheter. In addition, one patient with pneumothorax (1.0%) and one patient with infectious complications (1.0%) were identified, which was similar to that of a previous study of TBB alone [5]. Interestingly, most of the study patients received prophylactic antibiotics, and infectious complications occurred in only one patient who did not receive antibiotics. Generally, cryobiopsy causes more bleeding than forceps biopsy, and organized blood clots can block small airways, leading to obstructive pneumonia. Our findings suggest that oral prophylactic antibiotics can prevent infectious complications after cryobiopsy of PLLs.
The current study has some limitations. First, this study was conducted with a retrospective design at a single institution. Although a potential selection bias may have affected the study results, data from all subjects were consecutively collected. Second, reference data as a definitive histopathological diagnosis is insufficient. It is ideal to compare small biopsy results with surgical samples to verify false-positive results. In the present study, some patients were diagnosed with advanced malignant disease, such as lung metastasis from breast cancer, or refused surgical treatment. Therefore, we classified the malignant result of the bronchoscopy specimen as a definitive diagnosis. Although the probability is extremely low, false-positive results cannot be completely ruled out. Third, a pathological diagnosis was not established in 11 patients (10.0%). Furthermore, seven patients underwent regular CT scans for 12 months without additional procedures for tissue biopsy and were finally categorized as having benign disease, not otherwise specified. Although unlikely, malignancy may have been misclassified as benign based on the CT findings. Fourth, we evaluated the surface area of tissue samples by multiplying the longest diameter by its vertical diameter. However, this approach might not reflect the exact surface area of each sample, since there were heterogeneous features in the shape of the tissue sample.
In conclusion, sequential TBC using a novel 1.1-mm cryoprobe improved the performance of conventional TBB using RP-EBUS. Although procedure-related complications, such as bleeding, were relatively high, all patients were managed without life-threatening complications.
Electronic Supplementary MaterialSupplementary materials are available at Cancer Research and Treatment website (https://www.e-crt.org).
NotesEthical Statement This study was approved by the institutional review board of the Pusan National University Hospital (IRB No. 2112-027-110). Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study. Author Contributions Conceived and designed the analysis: Eom JS. Collected the data: Kim SH, Mok J, Eom JS. Contributed data or analysis tools: Kim SH, Mok J, Jo EJ, Kim MH, Lee K, Kim KU, Park HK, Lee MK, Eom JS. Performed the analysis: Kim SH, Mok J, Eom JS. Wrote the paper: Kim SH, Mok J, Eom JS. AcknowledgmentsThis work was supported by a clinical research grant from the Pusan National University Hospital in 2022. We thank Jinmi Kim and Jungmin Son (Department of Biostatistics, Clinical Trial Center, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital) for statistical advice.
Fig. 1Flow diagram of the study patients. EBUS, endobronchial ultrasound; PLL, peripheral lung lesion; TBB, transbronchial biopsy. 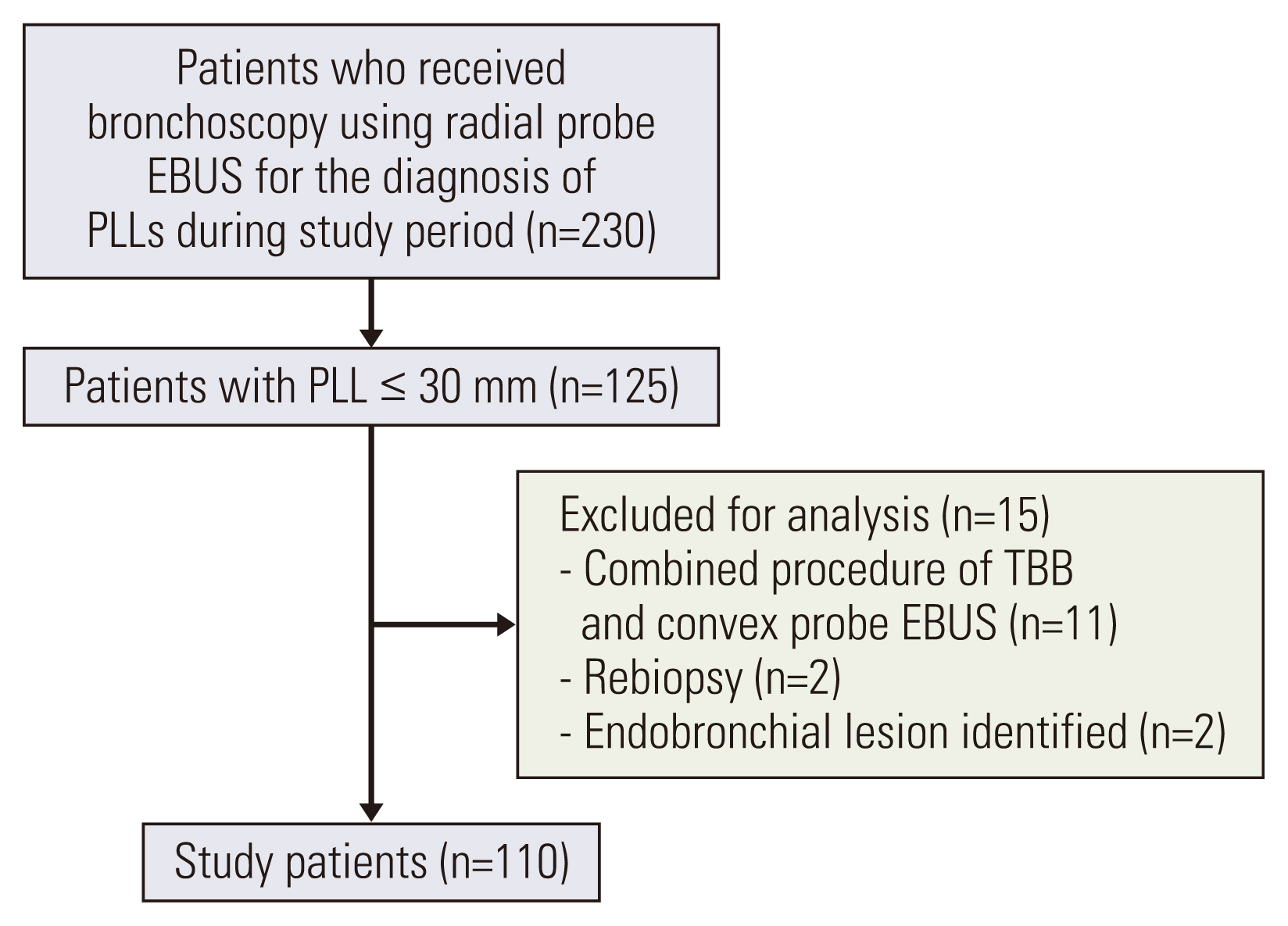
Fig. 3Comparisons of the mean longest diameter (A) and the surface area (B) of tissue between cyobiopsy samples and forceps biopsy samples. 
Table 1Baseline characteristics of the study patients
Table 2The final diagnosis of the study patients
Table 3Results of bronchoscopy variables Table 4Characteristics of patients with additional diagnostic benefits from cryobiopsy
References1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Church TR, Black WC, Aberle DR, Berg CD, Clingan KL, et al. Results of initial low-dose computed tomographic screening for lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1980–91.
2. Nanavaty P, Alvarez MS, Alberts WM. Lung cancer screening: advantages, controversies, and applications. Cancer Control. 2014;21:9–14.
3. Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, Mazzone PJ, Midthun DE, Naidich DP, et al. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e93S–120S.
4. Kurimoto N, Miyazawa T, Okimasa S, Maeda A, Oiwa H, Miyazu Y, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography using a guide sheath increases the ability to diagnose peripheral pulmonary lesions endoscopically. Chest. 2004;126:959–65.
5. Hayama M, Izumo T, Matsumoto Y, Chavez C, Tsuchida T, Sasada S. Complications with endobronchial ultrasound with a guide sheath for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions. Respiration. 2015;90:129–35.
6. Eom JS, Mok JH, Kim I, Lee MK, Lee G, Park H, et al. Radial probe endobronchial ultrasound using a guide sheath for peripheral lung lesions in beginners. BMC Pulm Med. 2018;18:137.
7. Ali MS, Trick W, Mba BI, Mohananey D, Sethi J, Musani AI. Radial endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respirology. 2017;22:443–53.
8. Schuhmann M, Bostanci K, Bugalho A, Warth A, Schnabel PA, Herth FJ, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided cryobiopsies in peripheral pulmonary lesions: a feasibility study. Eur Respir J. 2014;43:233–9.
9. Sryma PB, Mittal S, Madan NK, Tiwari P, Hadda V, Mohan A, et al. Efficacy of radial endobronchial ultrasound (R-EBUS) guided transbronchial cryobiopsy for peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPL’s): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pulmonology. 2021.
10. Yarmus LB, Semaan RW, Arias SA, Feller-Kopman D, Ortiz R, Bosmuller H, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a novel sheath cryoprobe for bronchoscopic lung biopsy in a porcine model. Chest. 2016;150:329–36.
11. Matsumoto Y, Nakai T, Tanaka M, Imabayashi T, Tsuchida T, Ohe Y. Diagnostic outcomes and safety of cryobiopsy added to conventional sampling methods: an observational study. Chest. 2021;160:1890–901.
12. Kuiper JL, Heideman DA, Thunnissen E, Paul MA, van Wijk AW, Postmus PE, et al. Incidence of T790M mutation in (sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;85:19–24.
13. Burgers JA, Herth F, Becker HD. Endobronchial ultrasound. Lung Cancer. 2001;34(Suppl 2):S109–13.
14. Kurimoto N, Morita K. Bronchial branch tracing. Singapore: Sprinter; 2020.
15. Ishida T, Asano F, Yamazaki K, Shinagawa N, Oizumi S, Moriya H, et al. Virtual bronchoscopic navigation combined with endobronchial ultrasound to diagnose small peripheral pulmonary lesions: a randomised trial. Thorax. 2011;66:1072–7.
16. Eberhardt R, Kahn N, Gompelmann D, Schumann M, Heussel CP, Herth FJ. LungPoint: a new approach to peripheral lesions. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1559–63.
17. Yamada N, Yamazaki K, Kurimoto N, Asahina H, Kikuchi E, Shinagawa N, et al. Factors related to diagnostic yield of transbronchial biopsy using endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath in small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Chest. 2007;132:603–8.
18. Hetzel M, Hetzel J, Schumann C, Marx N, Babiak A. Cryorecanalization: a new approach for the immediate management of acute airway obstruction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;127:1427–31.
19. Yoshikawa M, Sukoh N, Yamazaki K, Kanazawa K, Fukumoto S, Harada M, et al. Diagnostic value of endobronchial ultrasonography with a guide sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions without X-ray fluoroscopy. Chest. 2007;131:1788–93.
20. Kikuchi E, Yamazaki K, Sukoh N, Kikuchi J, Asahina H, Imura M, et al. Endobronchial ultrasonography with guide-sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:533–7.
21. Lee J, Kim C, Seol HY, Chung HS, Mok J, Lee G, et al. Safety and diagnostic yield of radial probe endobronchial ultrasound-guided biopsy for peripheral lung lesions in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Respiration. 2022;101:401–7.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||