AbstractPurposeDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common hematologic malignancy worldwide. Although substantial improvement has been achieved by the frontline rituximab-based chemoimmunotherapy, up to 40%–50% of patients will eventually have relapsed or refractory disease, whose prognosis is extremely dismal.
Materials and MethodsWe have carried out two prospective cohort studies that include over 1,500 DLBCL patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP (#NCT01202448 and #NCT02474550). In the current report, we describe the outcomes of refractory DLBCL patients. Patients were defined to have refractory DLBCL if they met one of the followings, not achieving at least partial response after 4 or more cycles of R-CHOP; not achieving at least partial response after 2 or more cycles of salvage therapy; progressive disease within 12 months after autologous stem cell transplantation.
ResultsAmong 1,581 patients, a total of 260 patients met the criteria for the refractory disease after a median time to progression of 9.1 months. The objective response rate of salvage treatment was 26.4%, and the complete response rate was 9.6%. The median overall survival (OS) was 7.5 months (95% confidence interval, 6.4 to 8.6), and the 2-year survival rate was 22.1%±2.8%. The median OS for each refractory category was not significantly different (p=0.529).
IntroductionDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common hematologic malignancy worldwide, accounting for 30%–40% of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cases. For patients with newly-diagnosed DLBCL, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard of care for nearly 20 years [1]. Although a number of efforts have been carried out to take up the position of the combination, virtually none has prevailed [2–4]. With R-CHOP treatment, up to 40%–50% of patients will expe-rience relapsed or refractory disease depending on several clinical indices, including the international prognostic index (IPI) [5] or molecular classifications [6].
The prognosis of patients who have experienced relapsed or refractory disease after R-CHOP treatment remains poor [7], and treatments consist of salvage chemotherapy with or without autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). However, for those with high-risk features, including failure after induction treatment or early relapse within 12 months, up to 50% of patients will eventually have disease progression even after ASCT [8]. The SCHOLAR-1 study analyzed 636 patients with refractory DLBCL and found that the objective response rate (ORR) was 26% to the next line of therapy, and the median overall survival (OS) was 6.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.9 to 7.0 months) [9]. Some of the recent advances may change the landscape of treatment of relapsed or refractory DLBCL (RR DLBCL) in the future [10–13]. Still, their accessibility and long-term outcomes need to be addressed, and it is crucial to select an optimal patient to benefit from the treatment. To define the outcomes of pati-ents with refractory DLBCL in Korea, we analyzed two prospective cohorts of DLBCL patients together.
Materials and Methods1. PatientsThe Consortium for Improving Survival for Lymphoma (CISL) has carried out two prospective cohort studies that include over 1,500 DLBCL patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP. The PROCESS cohort (#NCT01202448, CISL1006) comprises 595 DLBCL patients recruited from 26 tertiary institutes from August 2010 to August 2012 [14]. The primary endpoint of the cohort study was to evaluate the incidence and the risk factors for the secondary central nervous system involvement when treated with R-CHOP. The GIRAFFE-B cohort (#NCT02474550, CISL1403) has recruited 986 DLBCL patients from 24 tertiary institutes from January 2015 to April 2018. The cohort study’s primary endpoint was to evaluate the prophylactic effect of a pegylated granulocyte-colony stimulating factor against febrile neutropenia when treated with R-CHOP [15]. These cohort studies were approved by the institutional review board of the participating institutes.
In both cohorts, the diagnosis of DLBCL was established according to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification [16]. Patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma or primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma were excluded. After acquiring informed consent, patients were treated with standard R-CHOP21 up to 6–8 cycles. The treatment course could be shortened to 3–4 cycles in patients with stage I/II disease in which radiotherapy was planned. Follow-up data including survival and disease status were updated and centrally reviewed every 6 months. Among them, the criteria used in the SCHOLAR-1 study [9] was adopted to define refractoriness as follows: (1) no response during > 4 cycles of induction therapy; (2) no response during 2 cycles of salvage therapy; (3) relapse within 12 months from ASCT. Finally, patients who had been treated with subsequent therapy for the refractory disease were included in the analysis.
2. Statistical analysisThe common variables of the two cohort studies include age, sex, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, Ann-Arbor stage, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level, number of extranodal involvement, presence of B symptom(s), bone marrow involvement, and cell-of-origin classification by immunochemical stain using the Hans criteria [17].
In the GIRAFFE-B cohort, response to therapy was deter-mined by investigators according to the Lugano criteria incorporating positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET-CT) [18]. In contrast, PET-CT response was not assessed in the PROCESS cohort. Progression-free survival was calculated from commencing salvage treatment to the date of progression or death from any cause using the Kaplan-Meier methods. OS was calculated from starting salvage treatment to the date of death from any cause using the Kaplan-Meier methods. If a patient has experienced multiple refractoriness events, the date of commencing salvage treatment for the first event was regarded as starting date. Survivals were compared using the log-rank test, and Pearson’s λ2 test compared response rates. For all statistical analyses, p < 0.05 was considered significant, and the analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, ver. 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY).
Results1. Patient inclusionIn the PROCESS cohort, the complete or partial response from R-CHOP treatment was achieved in 534 patients (89.7%). The remaining 61 patients included those with stable disease (n=3), disease progression during treatment (n=38), and an undetermined response (n=20). After a median follow-up duration of 49.7 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 47.0 to 52.4), 151 cases were lost to follow-up, and 115 relapsed, or refractory disease cases were documented. Among them, a total of 57 patients were included in the refractory cohort for the following reasons: (1) no response during > 4 cycles of induction therapy (n=31); (2) no response during 2 cycles of salvage therapy (n=23); (3) relapse within 12 months from ASCT (n=3). In the GIRAFFE-B cohort, complete or partial response was achieved from R-CHOP treatment in 896 patients (90.9%). The remaining 90 patients included those with stable disease (n=13), disease progression during treatment (n=67), and an undetermined response (n=10). After a median follow-up duration of 44.1 months (95% CI, 42.0 to 46.2), 252 cases were lost to follow-up, and 202 relapsed or refractory disease cases were documented. Among them, a total of 203 patients were included in the refractory cohort for following reasons: (1) no response during > 4 cycles of induction therapy (n=71); (2) no response during 2 cycles of salvage therapy (n=110); (3) relapse within 12 months from ASCT (n=22). Collectively, 260 patients were included in the pooled analysis (Fig. 1).
2. Baseline characteristics of the refractory cohortAt the time of primary diagnosis of DLBCL, the median age was 63 (range, 22 to 85), and 166 patients (63.8%) were male. In terms of IPI risk group, 41 (15.8%), 66 (25.4%), 85 (32.7%), 68 (26.2%) were classified into low, low-intermediate (LI), high-intermediate (HI), and high-risk group, respectively. Bone marrow involvement was present in 53 patients (20.4%), and B symptom was present in 63 patients (24.2%). The cell-of-origin was available in 204 cases in which 69 (33.8%) and 135 patients (66.2%) were classified into germinal center B-cell (GCB) and non-GCB subtype, respectively. The details are described in Table 1.
Patients had the refractory disease at the median age of 65 years (range, 23 to 87 years) after a median time to progression of 9.1 months (95% CI, 7.8 to 10.4) from the start of R-CHOP treatment, of which median cycle of treatment was 6 (range, 1 to 8).
3. Salvage treatment regimens and their responsesResponse rates were similar between the two data sets, as overall response rates of the PROCESS and the GIRAFFE-B cohort were 24.0% and 27.1%, respectively (p=0.663). However, a complete response (CR) rate was slightly higher in the PROCESS cohort (14.0% vs. 9.9%), but it was not significantly different (p=0.442). Collectively, a CR rate was 9.6%, and an overall response rate was 26.4% (Table 2).
Platinum-based regimens including ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide, and dexamethasone), DHAP (cytarabine, cisplatin, dexamethasone), ESHAP/Ox (etoposide, methyl-prednisone, cytarabine, cisplatin or oxaliplatin), and GP/Ox (gemcitabine, cisplatin or oxaliplatin) were the most commonly used salvage regimens (n=228), which were followed by methotrexate-based ones (IMVP16: ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and prednisone; IVAM: ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine, and methotrexate; SMILE: etoposide, cyclophosphamide, asparaginase, and methotrexate; high-dose methotrexate; n=35) and bendamustine-rituximab (n=16). A total of 47 patients were treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, including rituximab (n=40) and ofatumumab (n=7). Overall response rates from the platinum-based regimens, methotrexate-based regimens, and bendamustine-rituximab were 26.3% (47/279), 31.2% (10/32), and 14.3% (2/14), which were not significantly different (p=0.125). Similarly, the addition of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies did not draw a significant difference (p=0.946) (Table 3).
4. Overall survivalThe median OS from the start of salvage treatment for the refractory disease was 7.5 months (95% CI, 6.4 to 8.6) (Fig. 2A). The 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival rates were 32.6% (±3.0%), 22.1% (±2.8%), and 21.2% (±2.8%), respectively. OS was consistently poor across the refractory category as OS for each subgroup, that is, (1) no response during > 4 cycles of induction therapy; (2) no response during 2 cycles of salvage therapy; (3) relapse within 12 months from ASCT were 7.5 months (95% CI, 5.2 to 9.8), 7.6 months (95% CI, 6.5 to 8.7), and 7.0 months (95% CI, 5.6 to 8.4), respectively (Fig. 2B). As expected, patients who had achieved CR demonstrated significantly prolonged OS compared to those who had achieved partial response or failed to achieve any response (not reached vs. 11.5 months [95% CI, 9.3 to 13.7] vs. 6.1 months [95% CI, 5.4 to 6.8], p < 0.001) (Fig. 2C). In terms of baseline characteristics, no variables including age, stage, number of extranodal involvement, or elevation of serum LDH could discriminate OS. Patients with GCB subtype (7.9 months; 95% CI, 5.6 to 10.2) showed trends for prolonged median OS compared to non-GCB subtype (6.6 months; 95% CI, 5.4 to 7.8; p=0.066) (Fig. 2D). Among 61 responders, 10 patients had undergone salvage ASCT, which did not result in OS difference (data not shown, p=0.297).
DiscussionThe present study analyzed the outcomes of refractory DLBCL after R-CHOP treatment. Out of 1,581 patients from the two prospective cohorts, 260 patients (16.4%) met the criteria for the refractory disease of the SCHOLAR-1 study [9]. However, only 26.4% of patients responded to subsequent salvage treatment, and the CR rate was 9.6%. Furthermore, the median OS from the start of salvage treatment for the refractory disease was 7.5 months (95% CI, 6.4 to 8.6) which was poor regardless of a subgroup of refractoriness or known baseline prognostic factors.
R-CHOP has been the standard of care for nearly 20 years. Though the combination has been validated for efficacy and safety, it is now regarded that up to 40%–50% of patients will relapse. For those who have relapsed or refractory disease, platinum-based salvage therapy with or without consolidating ASCT is the current standard of care depending on patients’ fitness. However, several factors, including low response rates of salvage treatment, the impracticability of ASCT due to age, performance status, or comorbidity, and frequent relapses after ASCT frequently render a group of patients succumbs to the disease. Recent advances, including chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies [10], CD19-targeting antibodies [11], antibody-drug conjugates [12], and bispecific antibodies [13], have dramatically improved outcomes of patients with RR DLBCL as some of them may expect long-term remission of the disease. One of the major concerns is the treatment feasibility, which should be considered both in terms of cost and facility. Thus, it is important to select an optimal patient for whom those treatments are required most.
The outcomes depend on the relapse timing, as patients with early relapse show significantly poor compared to patients with late relapse [19]. For instance, in the CORAL study, patients with the relapsed disease within 12 months showed substantially lower response rate (46% vs. 88%), 3-year event-free survival rate (20% vs. 45%), and 3-year OS rate (39% vs. 64%) compared to patients with relapsed disease after 12 months when treated with rituximab combined with either ICE or DHAP [7]. Similarly, the duration of remission after ASCT was significantly associated with OS in DLBCL patients [20]. Collectively, early treatment failure is universally regarded as one of the single most predictive markers for poor survival. In the SCHOLAR-1 trial, which was the basis of the current study, refractoriness was defined as (1) no response during > 4 cycles of induction therapy; (2) no response during 2 cycles of salvage therapy; (3) relapse within 12 months from ASCT [9]. The poor outcomes were observed across the subgroups, as the response rates ranged from 20% to 34%, and the median OS ranged from 6.1 months to 7.1 months. A recently published Chinese study that adopted the same criteria as the SCHOLAR-1 study demonstrated similar findings [21]. In 350 patients with refractory DLBCL, the ORR of the subsequent treatment was 30%, and the CR rate was 9%. The median OS was 5.9 months (95% CI, 5.5 to 7.1), and the 2-year OS rate was 16% (Table 4). Given that these poor outcomes are very similar to those of the current study, the criteria of the SCHOLAR-1 study seem to be suitable for determining refractory patients, and patients who meet the criteria should strongly be considered for the candidate of novel treatment.
To define the high-risk DLBCL, several prognostic indices have been used including IPI. In the current study, 107 (41.2%) and 153 (58.8%) patients were categorized into low/LI - and HI/high-risk groups, respectively. In the two original cohorts, the numbers of the patient in the relevant group were 1,001 (63.3%) and 580 (36.7%), respectively, which can be translated into an odds ratio of 2.99 (95% CI, 2.28 to 3.94) of developing refractory disease for patients with HI/high-risk patients. However, once the refractory disease developed, no variables including age, stage, number of extranodal involvement, or elevation of serum LDH could probably discriminate OS, as they were collected at the time of initial disease diagnosis, not after the determination of refractory disease. Interestingly, the cell-of-origin classification that is not expected to be changed during treatment showed some impact on survival. Patients with the GCB subtype showed trends for prolonged OS compared to the non-GCB subtype (median, 7.9 vs. 6.6 months; p=0.066).
The optimal salvage treatment has not been determined for RR DLBCL patients. However, platinum-based regimens including ICE, DHAP, ESHAP, or DHAP have been widely accepted as a standard of treatment, and they have been used interchangeably. In the current study, the platinum regimens were the most frequently used treatment (n=202), as expected. Still, several other combinations, including methotrexate-based (n=35) or bendamustine-based (n=16) regimens, were also used, among which no significantly different response rates were observed. The use of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody also did not impact on response rate suggesting the necessity of novel treatments such as CD19 or CD79b targeting therapies in this setting. Although OS difference in the current study was not observed between salvage therapy followed by ASCT (n=10) and chemo-only arm (n=51), that may be contributed from the small number of the subset and insufficient response before ASCT (only 5 of the 10 patients achieved CR and proceeded to ASCT). Indeed, in these high-risk patients, the benefit of ASCT after salvage treatment was shown in larger-scaled trials [9,21]. Thus, early administration of ASCT for high-risk patients may be recommended to overcome the poor outcome of patients with RR DLBCL.
The current study has several limitations. First, a relatively large portion of the patient was lost to follow-up. Of the 1,581 patients, 403 (25.5%) were lost to follow-up during or immediately after R-CHOP treatment. Although the reasons are unknown, some of these losses could have been due to the rapidly progressive disease. Second, immunohistochemical features including double-expressor status and cytogenetic features including double-hit status as well as molecular profiles have not been collected. Thus, their roles in the development of refractory disease could not be assessed. Third, the responses were examined by individual investigators. However, as we assessed OS, we believe the conclusive data have validity.
In conclusion, this study confirms the devastating prognosis of patients with refractory DLBCL defined by the SCHOLAR-1 study. They were not likely to respond to subsequent treatment with the ORR of 26% and were inevitably associated with poor survival with the median OS barely exceeding 7 months. Therefore, these patients should promptly be approached to novel therapies.
NotesEthical Statement The protocol was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board of each participating center, and all patients provided written informed consent before treatment initiation; Gachon University Gil Medical Center: GCIRB2015-74, Gyeongsang National University Hospital: GNUH 2015-02-012, Dongsan Medical Center: DSMC 2015-03-015, Korea University Anam Hospital: ED15-024(AN15024-001), Kosin University Gospel Hospital: KUGH 2017-09-008, National Cancer Center: NCC 2015-0091, Dong-A University Medical Center: DMC 15-037, Pusan National University Hospital: H-1701-011-051, Samsung Medical Center: SMC 2014-07-181, Seoul National University Hospital: H-1504-119-667, Asan Medical Center: S2015-0302-0001, Soonchunhyang University Hospital: SCHUH 2015-05-007, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital: SCHBC 2015-07-008, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital: CR315002-002, Ajou University Hospital: AJIRB-MED-OBS-14-254, Yeungnam University Medical Center: YUMC 2015-03-016, Korea Cancer Center Hospital: K-1409-001-001, Ulsan University Hospital: UUH 2015-11-007, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital: SGPAIK 2015-06-002, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital: ISPAIK 2015-07-002, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital: BS 2015-0110, Jeonbuk National University Hospital: CUH 2015-02-034, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital: TMP-2015-023, Chung-Ang University Hospital: C2015048(1506), Chungnam National University Hospital: CNUH 2015-10-060, Chungbuk National University Hospital: CBNUH 2015-03-006, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital: HUH 2015-I043. Author Contributions Conceived and designed the analysis: Yi JH, Jeong SH, Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Koh Y, Kim JS. Collected the data: Lee WS, Yang DH, Do YR, Kim MK, Yoo KH, Choi YS, Yun WJ, Park Y, Jo JC, Park BB, Kang HJ, Yun WJ, Kwon JH, Hong DS, Lee HS, Lee GW. Contributed data or analysis tools: Eom HS, Kwak JY, Shin HJ, Yi SY, Oh SY, Kim HJ, Sohn BS, Won JH. Performed the analysis: Yi JH, Suh C. Wrote the paper: Yi JH, Kim WS. Fig. 1Patient inclusion and flow diagram. ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CR, complete response; NE, not evaluable; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease. 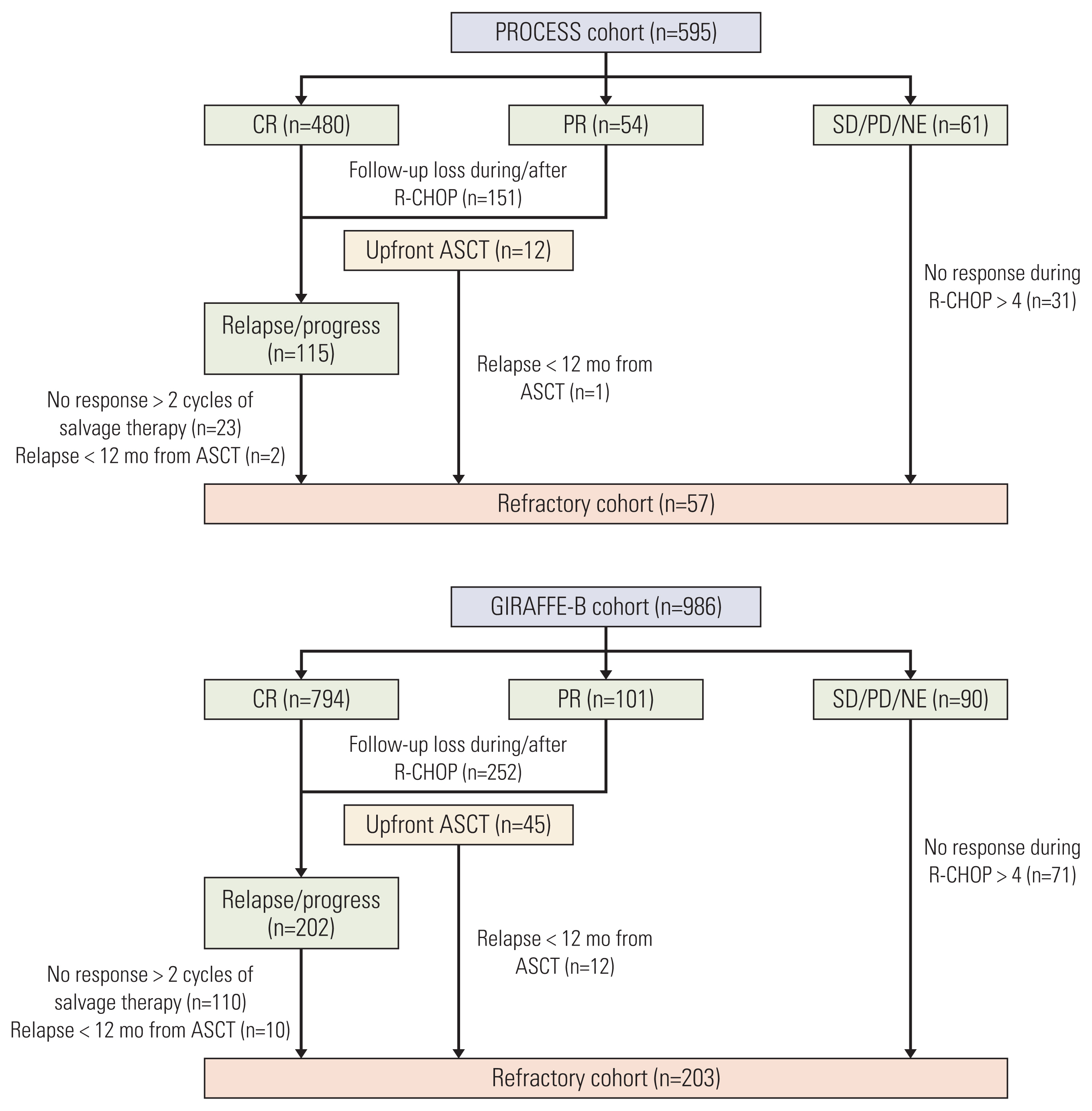
Fig. 2Overall survival from commencement of salvage therapy: overall population (A); by refractory category (B); by tumor response (C); by cell-of-origin subtype (D). ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CR, complete response; GCB, germinal center B-cell; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease. 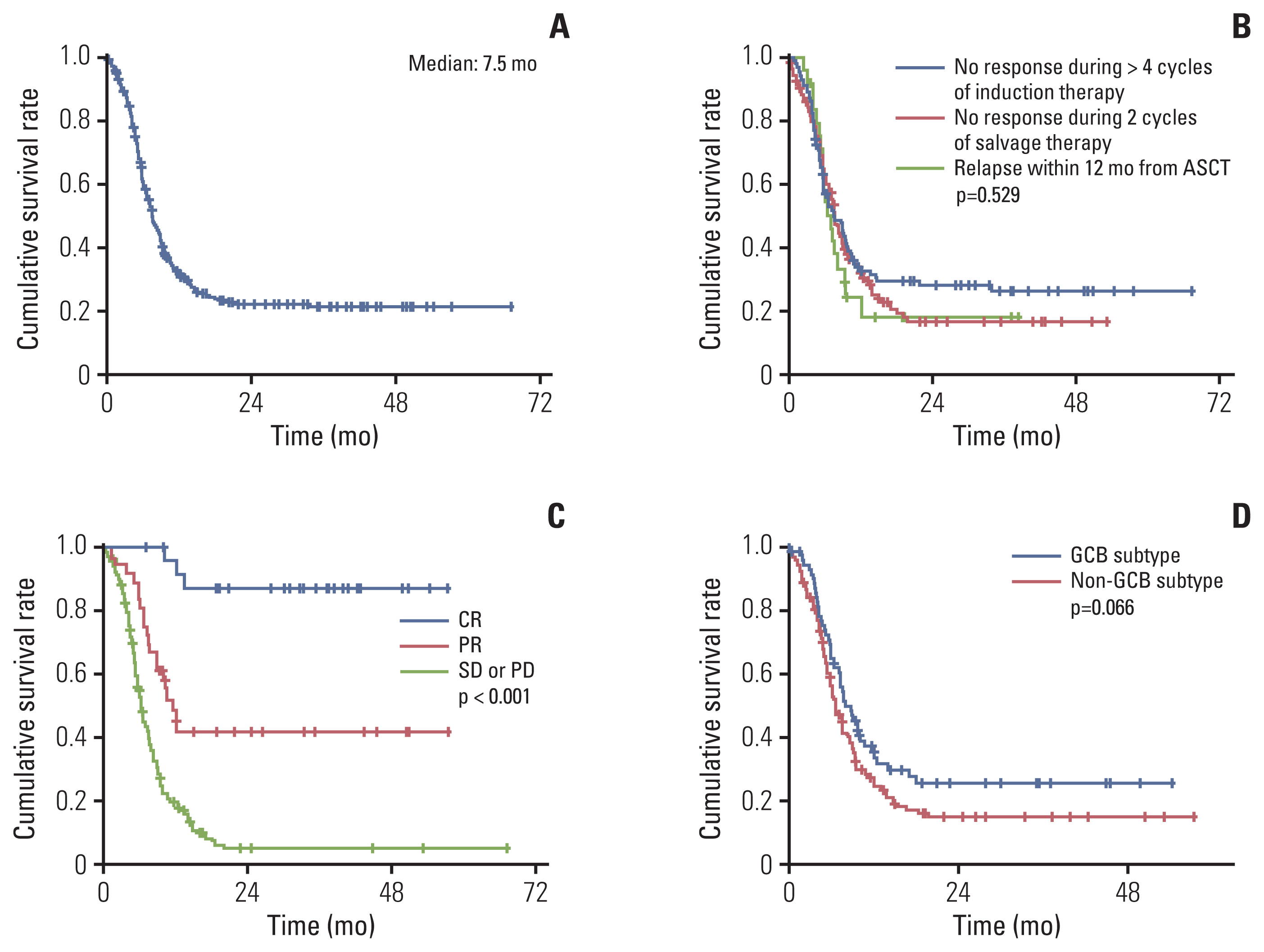
Table 1Baseline characteristics of the refractory cohort (n=260) Table 2Response to chemotherapy after refractory disease Table 3Response according to salvage regimens Values are presented as number (%). Platinum-based regimens include ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide, and dexamethasone), DHAP (cytarabine, cisplatin, dexamethasone), GDP (gemcitabine, cisplatin, and dexamethasone) and ESHAP/Ox (etoposide, methyl-prednisone, cytarabine, cisplatin or oxaliplatin); Methotrexate-based regimens include IMVP16 (ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and prednisone), IVAM (ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine, and methotrexate), and high-dose methotrexate; bendamustine-based regimens include benda-mustine with or without rituximab; miscellaneous regimens included brentuximab-vedotin (n=1), CODOX-M/IVAC (n=1), HyperCVAD (n=2), ibrutinib (n=1), and tafasitamab (n=2). CR, complete response; PR, partial response. Table 4Outcomes of patients with refractory DLBCL who met the criteria of the SCHOLAR-1 study
References1. Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:235–42.
2. Vitolo U, Trneny M, Belada D, Burke JM, Carella AM, Chua N, et al. Obinutuzumab or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone in previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3529–37.
3. Bartlett NL, Wilson WH, Jung SH, Hsi ED, Maurer MJ, Pederson LD, et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R compared with R-CHOP as frontline therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: clinical outcomes of the phase III intergroup trial alliance/CALGB 50303. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1790–9.
4. Nowakowski GS, Chiappella A, Gascoyne RD, Scott DW, Zhang Q, Jurczak W, et al. ROBUST: a phase III study of lenalidomide plus R-CHOP versus placebo plus R-CHOP in previously untreated patients with ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1317–28.
5. International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:987–94.
6. Schmitz R, Wright GW, Huang DW, Johnson CA, Phelan JD, Wang JQ, et al. Genetics and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1396–407.
7. Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M, et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4184–90.
8. Hamadani M, Hari PN, Zhang Y, Carreras J, Akpek G, Aljurf MD, et al. Early failure of frontline rituximab-containing chemo-immunotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma does not predict futility of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1729–36.
9. Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130:1800–8.
10. Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531–44.
11. Salles G, Duell J, Gonzalez Barca E, Tournilhac O, Jurczak W, Liberati AM, et al. Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): a multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:978–88.
12. Sehn LH, Herrera AF, Flowers CR, Kamdar MK, McMillan A, Hertzberg M, et al. Polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:155–65.
13. Hutchings M, Morschhauser F, Iacoboni G, Carlo-Stella C, Offner FC, Sureda A, et al. Glofitamab, a novel, bivalent CD20-targeting T-cell-engaging bispecific antibody, induces durable complete remissions in relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoma: a phase I trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1959–70.
14. Kim SJ, Hong JS, Chang MH, Kim JA, Kwak JY, Kim JS, et al. Highly elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase is associated with central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of a multicenter prospective cohort study. Oncotarget. 2016;7:72033–43.
15. Hyun JS, Kim SJ, Hong JY, Koh Y, Kang HJ, Park Y, et al. A prospective registry study of Peg-G-CSF prophylaxis for pati-ents with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (CISL 1403). Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):2840.
16. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H. WHO classification of tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008.
17. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004;103:275–82.
18. Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059–68.
19. Vannata B, Conconi A, Winkler J, Cascione L, Margiotta Casaluci G, Nassi L, et al. Late relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: impact of rituximab on their incidence and outcome. Br J Haematol. 2019;187:478–87.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||