Detection of Germline Mutations in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Using Multi-gene Panels: Beyond BRCA1/2
Article information
Abstract
Purpose
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows simultaneous sequencing of multiple cancer susceptibility genes and may represent a more efficient and less expensive approach than sequential testing. We assessed the frequency of germline mutations in individuals with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), using multi-gene panels and NGS.
Materials and Methods
Patients with EOC (n=117) with/without a family history of breast or ovarian cancer were recruited consecutively, from March 2016 toDecember 2016.GermlineDNAwas sequenced using 35-gene NGS panel, in order to identify mutations. Upon the detection of a genetic alteration using the panel, results were cross-validated using direct sequencing.
Results
Thirty-eight patients (32.5%) had 39 pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations in eight genes, including BRCA1 (n=21), BRCA2 (n=10), BRIP1 (n=1), CHEK2 (n=2), MSH2 (n=1), POLE (n=1), RAD51C (n=2), and RAD51D (n=2). Among 64 patients with a family history of cancer, 27 (42.2%) had 27 pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations, and six (9.3%) had mutations in genes other than BRCA1/2, such as CHECK2, MSH2, POLE, and RAD51C. Fifty-five patients (47.0%) were identified to carry only variants of uncertain significance.
Conclusion
Using the multi-gene panel test, we found that, of all patients included in our study, 32.5% had germline cancer-predisposing mutations. NGS was confirmed to substantially improve the detection rates of a wide spectrum of mutations in EOC patients compared with those obtained with the BRCA1/2 testing alone.
Introduction
The evaluation of germline mutations in high-penetrance epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) predisposition genes, specifically BRCA1 and BRCA2 (BRCA1/2), has become a standard clinical practice. Lifetime estimates of EOC risk range from 24% to 59% and 8% to 35% in BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers, respectively [1-4]. Identification of BRCA1/2 mutations allows the application of preventive strategies, including breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) screening or risk-reducing surgeries, which can improve survival [5,6].
With the advances in the next-generation sequencing (NGS), simultaneous sequencing of multiple cancer susceptibility genes beyond BRCA has become available through multi-gene panel testing in a less expensive and more rapid manner, compared with that of the single-gene testing [7]. Additionally, testing multiple genes simultaneously creates the potential for unexpected findings as well as for the identification of genetic alterations for which the clinical management has not been established yet [7-9]. Previous investigations of germline mutations using multi-gene panel testing of EOC patients revealed that 18%-24% of patients carry germline mutations in BRCA1/2, BARD1, BRIP1, CHEK2, MRE11A, MSH6, NBN, PALB2, RAD50, RAD51C, RAD51D, or TP53 genes [7,9]. Furthermore, in one study, which included 127 EOC patients who previously underwent noninformative genetic screening, nine patients (7%) were found to have pathogenic mutations in APC, ATM, BRCA2, BRIP1, MUTYH, and RAD51D genes [8].
However, considering the ethnicity-specific differences in the germline mutations in cancer susceptibility genes, the assessment of cancer susceptibility gene variants in all ethnic groups using clinical data is necessary. In Asians, no previous studies evaluated the frequency of germline mutations in cancer susceptibility genes other than BRCA1/2 genes in individuals with EOC who were referred for genetic evaluation.
The primary objective of this study was to investigate the frequency and spectrum of germline mutations in 35 cancer susceptibility genes using multi-gene panel testing in a population of consecutive Korean patients with EOC.
Materials and Methods
1. Patient selection
All women with EOC admitted to Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, South Korea, between March 2016 and December 2016, who consented to multi-gene panel testing for clinical research, were included in this study. Blood samples of the participants were obtained, and the clinical and pathologic data abstracted from medical records included personal and family cancer histories, cancer histology, stage, ancestry, and previous genetic test results. All ovarian cancers were reviewed by a gynecologic pathologist panel at the same institute. Genetic test results obtained in this study were considered research results and were not returned to study participants or utilized for clinical decision making.
2. NGS assay
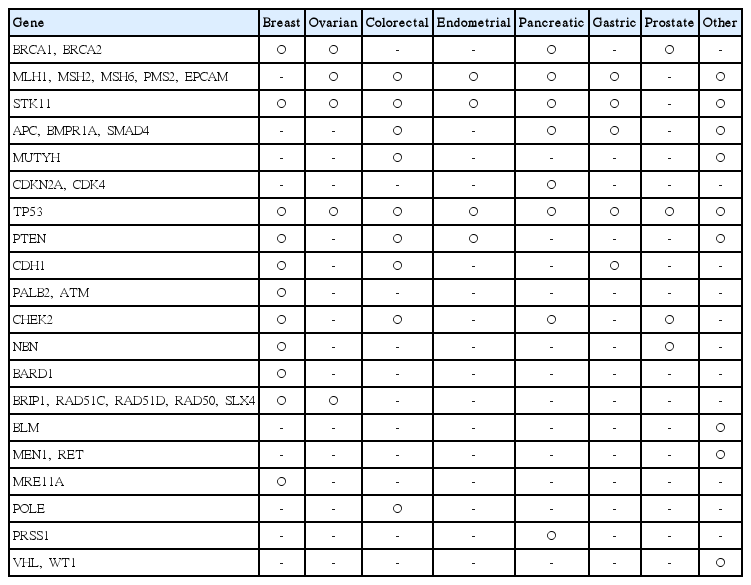
Germline DNA was extracted from peripheral blood sample of the participants using the QIAamp Blood DNA mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Intact DNA was quantified and adjusted to the concentration of 5 ng/μL using a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA) and the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Invitrogen). Precapture libraries were constructed according to the manufacturer’s sample preparation protocol. Genomic DNA of each patient was fragmented to a median size of 300 bp. We used customized targeted capture sequencing panel (OncoRisk, Celemics, Seoul, Korea) covering all coding sequences and intron-exon boundaries of the coding exons of 35 cancer susceptibility genes, including BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, BARD1, BRIP1, RAD51C, RAD51D, RAD50, NBN, MRE11A, ATM, CHEK2, TP53, PTEN, APC, BLM, BMPR1A, CDH1, CDK4, CDKN2A, EPCAM, MEN1, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, MUTYH, PMS2, POLE, PRSS1, RET, SLX4, SMAD4, STK11, VLH, and WT1. DNA fragments were end-repaired, phosphorylated, and adenylated at the 3′ ends. The index adaptors were ligated to the repaired ends, DNA fragments were amplified, and fragments of 200 to 500 bp were isolated. Pooled libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA) using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (300 cycles).
3. NGS data analysis
All clinically actionable variants identified by NGS, as well as regions that did not meet our preset NGS quality metrics, were independently confirmed with orthogonal site-specific Sanger sequencing. Analyzed genes were categorized according to the cancer type-predisposing mutations (Table 1).
4. Annotation and variant classification
Variants were described according to nomenclature recommendations of the Human Genome Variation Society (http://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen) and further categorized according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics recommendations, with supporting linkage, biochemical, clinical, functional, and statistical data used for specific missense and intronic alterations [10-12]. The variants were classified into pathogenic, likely pathogenic, variant of uncertain significance (VOUS), likely benign, and benign/polymorphism, using five-tier system following the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics [10]. Initially, variants were filtered by their frequencies in population control databases including ExAC (non‒The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset; frequencies were calculated according to the ethnic subgroups), ESP6500, 1000 Genomes Project, and Korean Reference Genome Database. Variants with a minor allele frequency (MAF) greater than 5% in any of the population subgroups were classified as absolutely benign. Conventionally, variants with a MAF greater than 0.5% were considered as having a strong evidence for a benign variant, whereas the evidence supporting pathogenicity was considered moderate if these variants were shown to be absent from the general population. Furthermore, literature and database search for previous reports and functional studies was performed using Alamut Visual 2.6 software (Interactive Biosoftware, Rouen, France) and Human Gene Mutation Database professional database. When all in silico analyses showed consistent predictions, the results were considered the evidence demonstrating that a certain variant is benign or pathogenic.
5. Confirmation by other methods
We identified all small base pair variations using Sanger sequencing on a 3730 DNA Analyzer with the BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Sequencing data were aligned against appropriate reference sequences and analyzed using the Sequencher 5.3 software (Gene Codes Corp., Ann Arbor, MI). Chromosomal copy number alterations were confirmed using the Infinium CytoSNP 850K array (Illumina) and BlueFuse Multi software (Illumina).
6. Ethical statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Yonsei University College of Medicine (No. 4-2015-0141) and performed in accordance with the ethical standards described in the Declaration of Helsinki. The requirement to obtain a written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board of the Yonsei University College of Medicine because our study was retrospective research based on medical records, and this research presented no more than minimal risk of harm to subjects.
Results
1. Study population
In Fig. 1, the results of multi-gene panel testing are presented. Of 117 patients with EOC, 44 deleterious mutations were identified in 38 (32.5%) women, and 55 patients (47.0%) were revealed to carry only VOUSs in 34 genes. Multiple genetic mutations were concomitantly identified in a patient. Clinical and tumor pathologic features of study participants per state of mutation are shown in Table 2. Out of 38 patients with pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations, 31 had BRCA1/2 mutation and eight were shown to carry non-BRCA1/2 mutations. All the BRCA1/2 mutations detected in NGS assay were also confirmed by Sanger sequencing. The median age at diagnosis was 52 years (range, 16 to 83 years); 99.1% of the study population was Asian, and 0.9% was non-Ashkenazi white; 71.8% of the patients had stage III or IV disease. Furthermore, 54.7% of patients reported having a first-degree relative with cancer. In total, 64 patients (54.7%) had a family history of cancer, and among 38 patients who carried deleterious mutations in genes, 25 patients (65.8%) had family history of cancer in first-degree relatives. Concurrent breast cancers were found in seven patients (6%), and five of them carried BRCA1 mutation, while one carried BRCA2. There were no significant differences in the clinicopathologic characteristics between patients with BRCA1/2 mutation and patients with non-BRCA1/2 mutation. Also, Kaplan-Meier analysis showed there were no differences in progression-free survival (p=0.567) and overall survival (p=0.492) between the two groups (S1 Fig.)

Multiple-gene panel testing results. In a patient, multiple mutations were concomitantly identified. EOC, epithelial ovarian cancer; VOUS, variants of uncertain significance. a)Two mutations including BRCA1 and one non-BRCA1/2 gene were identified simultaneously in a patient.
2. Frequency and spectrum of pathogenic and likely pathogenic mutations
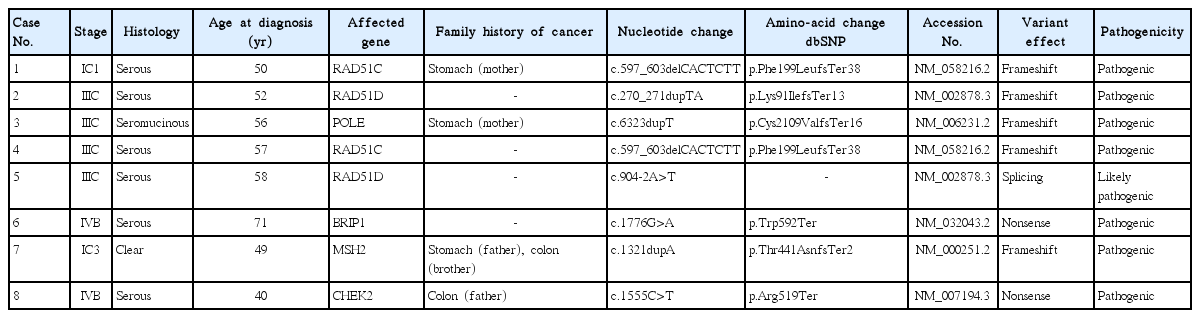
Frequency of genetic alterations, including pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations and VOUSs, is illustrated in Fig. 2. All the data with anonymized and deidentified patient information is available in S2 Table. Among 117 patients with EOC, 39 pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations were identified in 38 women (32.5%). Out of 39 germline mutations detected, 31 (79.5%) were shown to be germline BRCA1/2 mutation, 21 in BRCA1, and 10 in BRCA2. In addition, eight (6.8%) women had a total of eight deleterious mutations in non-BRCA1/2 cancer predisposition genes including BRIP1 (n=1), CHEK2 (n=1), MSH2 (n=1), POLE (n=1), RAD51C (n=2), and RAD51D (n=2). Characteristics of patients with non-BRCA1/2 mutations are presented in Table 3.

Proportion of pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations and variants of uncertain significance (VOUSs). (A) Multigene panel test results. (B) Proportion and number of pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations.
We did not find any deleterious mutations in APC, ATM, BARD1, BLM, BMPR1A, BMPR1B, CDH1, CDH2, CDKN2A, EPCAM, MEN1, MRE11A, MLH1, MSH6 MUTYH, NBN, PALB2, PMS2, PRSS1, RAD50, RET, SLX4, STK11, TP53, VHL, or WT1 genes.
3. Frequency of VOUSs in cancer susceptibility genes
Clinical and tumor pathologic features of study participants per state of VOUS are presented in S3 Table. Frequency and spectrum of identified VOUSs are illustrated in Fig. 3. At least one VOUS was identified in 78 women (66.7%), and 145 VOUSs have been identified in total. Twenty-five patients with VOUS also had a concomitant deleterious mutation. Among 54 patients (46.2%) that carried only VOUSs, 30 patients had a family history of cancer in the first-degree relatives.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that included consecutively enrolled EOC patients of the Asian ethnicity, and retrospectively examined the frequency and spectrum of germline mutations in BRCA1/2 and other cancer predisposition genes. Among 117 patients, we found that 38 patients (32.5%) carried pathogenic and likely pathogenic mutations, while eight patients (6.8%) were shown to have mutations in non-BRCA1/2 cancer predisposition genes, including BRIP1, CHEK2, MSH2, POLE, RAD51C, and RAD51D.
A large-scale study presented spectrum of germline mutations of ovarian cancer patients, whose ethnicities were predominantly non-Hispanic whites (87.4%) [9]. The research reported germline mutations in BRIP1 (1.4%), RAD51C (0.6%), RAD51D (0.6%), MLH1 (0.01%), and CHEK2 (0.06%), which also found in our study. [9] However, considering the extensive gap between the numbers of subjects (1,915 patients vs. 117 patients), a direct comparison with our results is not acceptable. NGS panel test for patients with EOC began to be covered by National Health Insurance from March 2017, systematic gathering and analysis of the produced data from ovarian cancer patients with Korean ethnicity are required to compare with the data from another ethnicity.
RAD51C and RAD51D are known to correlate with an increased risk of EOC due to their involvement in the Fanconi-BRCA pathway [13,14]. RAD51C mutations are found in 1% of unselected EOC patients and confer an overall lifetime EOC risk of about 9% at an average onset age of 60 years [14]. A previous population-based case-control study demonstrated that RAD51C and RAD51D represent moderate EOC susceptibility genes, and 18% of EOCs (more frequently in high-grade serous type) carrying RAD51C and RAD51D mutations developed at age 50 or younger. If this risk estimate is confirmed, risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy may be a beneficial option for premenopausal women [15]. We identified four participants with pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations, including RAD51C c.597_603delCACTCTT (p.Phe199LeufsTer38), RAD51D c.270_271dupTA (p.Lys91IlefsTer13), and RAD51D c.904-2A>T.
BRCA1-interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (BRIP1) is involved in the BRCA-Fanconi anemia pathways, and it was identified as a moderate-penetrance gene, conferring an increased risk for EOC, with 6-8-fold increased EOC risk and 10%-15% lifetime risk [16,17]. Another report demonstrated that BRIP1 mutations were found in 1.4% of EOC patients, and they were shown to be associated with a moderate increase in EOC risk. These data have clinical implications for the development of preventive strategies for the BRIP1 mutation carriers [18]. We identified one patient in our study as a carrier of a deleterious mutation, BRIP1 c.1776G>A (p.Trp592Ter), who has no family history of cancer in the first-degree relatives.
Cell-cycle checkpoint kinase 2 (CHEK2) plays a role in cell-cycle arrest and DNA repair and its mutations contribute to the development of hereditary and sporadic cancers [19]. One meta-analysis showed that CHEK2 1100delC increases the lifetime risk 3-5 folds, with a 37% increase in the cumulative risk of breast cancer by the age of 70 [20]. A previous study examining Asian population reported that CHEK2 c.1111C>T (p.His371Tyr, rs531398630) was detected in familial and unselected breast cancer cases and controls, with 4.24% (5/118), 1.76% (16/909), and 0.73% (9/1228), respectively [21]. In this study, we identified two EOC patients (age, 31 and 40 years) with pathogenic mutation, CHEK2 c.1111C>T (p.His371Tyr) and c.1555C>T (p.Arg519Ter), and a family history of hematologic cancer and colon cancer in the first-degree relatives, respectively. The patients were referred to the department of breast surgery, and followed up with regular surveillance using breast MRI.
The benefit of genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations is well established. In addition to cancer prevention strategies such as risk-reducing surgery, BRCA-associated cancers were confirmed to show a better response to therapies such as poly(ADP) ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors and platinum agents than sporadic cancers [22,23]. Considering the role of BRIP1, CHEK2, RAD51C, and RAD51D in the BRCA pathway responsible for DNA repair, EOCs in patients with mutations in BRIP1, CHEK2, RAD51C, or RAD51D may represent potential targets for PARP1 inhibitors, similar to the BRCA1/2 mutation carriers.
The usefulness of multi-gene panel testing aimed at the detection of germline mutations would be more beneficial for the familial surveillance and risk-reduction strategies, rather than the application of a targeted therapy, such as PARP1 inhibition therapy. Currently, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy when known mutations in the EOC-associated genes (BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1, MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, and PMS2) are detected [24]. Additionally, risk-reducing mastectomy is recommended when known breast cancer–associated gene (BRCA1, BRCA2, CDH1, PTEN, TP53, and PALB2) mutations are identified. Furthermore, the mutations in ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CDH1, CHEK2, PLAB2, PTEN, STK11, and TP53 suggest that the subsequent screening using breast MRI may be indicated [24].
Mutations in the mismatch repair genes (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM), which cause Lynch syndrome, are often considered the major causes of hereditary EOC, in addition to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations [25]. The identification of these mutations may allow an improved surveillance, leading to the identification of colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, and other cancers in patients with EOC and their relatives [26]. An MSH2mutation, c.1321dupA (p.Thr441AsnfsTer2), was detected in our study, and the patients had sigmoid colon cancer concomitantly with the family history of stomach cancer. Further large population-based studies are required to establish the frequency of deleterious mutations in these genes.
We detected a non-hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome related gene, POLE. The POLE gene mutation was reported as a risk factor for the early onset mismatch repairdeficient colorectal cancer [27]. According to the NCCN guidelines, enhanced colorectal cancer screening is recommended in patients with a germline mutation in POLE gene.
According to the data collected in this study, 78 patients (66.7%) were shown to have 145 VOUSs in 34 genes (Fig. 3). Approximately one-third of patients had at least one VOUS, as previously reported in other studies evaluating NGS panels [4,26]. Most of them will eventually be categorized, most likely as benign, but some will be categorized as deleterious [12,28]. Until their significance is fully understood, VOUSs should not be used for making clinical decisions.
The application of multi-gene panel testing in the evaluation of cancer susceptibility genes has been rapidly increasing in clinical practice. These multi-gene panel tests can be used for the analysis of not only high-penetrance genes with established clinical utility, but also genes for which clinical validity or significance is currently less evident. The appropriate interpretation of results is important for the development and recommendation of effective strategies for risk management, which may be challenging for clinicians, who often lack genetic training, and for their patients, who should undergo the screening and prevention strategy decision-making process.
In conclusion, here we presented germline mutation data obtained from unselected EOC patients of Asian ethnicity. Overall, 38 out of 117 EOC patients (32.5%) were shown to have 39 germline mutations in eight genes (BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CHEK2, MSH2, POLE, RAD51C, and RAD51D). We identified non-BRCA1/2 cancer predisposition genes mutation in eight out of 117 patients (6.8%). NGS has a potential to substantially improve the detection rates of a wide spectrum of mutations in ovarian cancer patients compared with the BRCA1/2 testing alone.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials are available at Cancer Research and Treatment website (http://www.e-crt.org).
Notes
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2014R1A1A1A05002926, 2017R1A2B4005503).