AbstractPurposeThere are clinical unmet needs in predicting therapeutic response and precise strategy for the patient with advanced biliary tract cancer (BTC). We aimed to identify genomic alterations predicting therapeutic response and resistance to gemcitabine and cisplatin (Gem/Cis)-based chemotherapy in advanced BTC.
Materials and MethodsGenomic analysis of advanced BTC multi-institutional cohorts was performed using targeted panel sequencing. Genomic alterations were analyzed integrating patients’ clinicopathologic data, including clinical outcomes of Gem/Cis-based therapy. Significance of genetic alterations was validated using clinical next-generation sequencing (NGS) cohorts from public repositories and drug sensitivity data from cancer cell lines.
Results193 BTC patients from three cancer centers were analyzed. Most frequent genomic alterations were TP53 (55.5%), KRAS (22.8%), ARID1A (10.4%) alterations, and ERBB2 amplification (9.8%). Among 177 patients with BTC receiving Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy, ARID1A alteration was the only independent predictive molecular marker of primary resistance showing disease progression for 1st-line chemotherapy in the multivariate regression model (odds ratio, 3.12; p=0.046). In addition, ARID1A alteration was significantly correlated with inferior progression-free survival on Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy in the overall patient population (p=0.033) and in patients with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) (p=0.041). External validation using public repository NGS revealed that ARID1A mutation was a significant predictor for poor survival in BTC patients. Investigation of multi-OMICs drug sensitivity data from cancer cell lines revealed that cisplatin-resistance was exclusively observed in ARID1A mutant bile duct cancer cells.
ConclusionIntegrative analysis with genomic alterations and clinical outcomes of the first-line Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy in advanced BTC revealed that patients with ARID1A alterations showed a significant worse clinical outcome, especially in extrahepatic CCA. Well-designed prospective studies are mandatory to validate the predictive role of ARID1A mutation.
IntroductionBiliary tract cancer (BTC) is a heterogeneous disease harboring several disease entities in terms of anatomical locations of tumor including extrahepatic, intrahepatic, and gallbladder lesions, with poor prognosis. Although BTCs are not among the most common cancers, their incidence is relatively high in Asia, and it has been reported that its incidence has been recently increasing [1]. Surgery is the only current curative treatment, but most patients are diagnosed with unresectable disease. Systemic chemotherapy is thus the standard of care for patients with advanced BTC. Since 2010, the combination of gemcitabine and cisplatin (Gem/Cis) has prevailed as the standard first-line systemic treatment for advanced BTC [2].
For a long time, the infrequency and heterogeneity of the different BTC subtypes have limited clinical therapeutic progress in advanced BTC. Nevertheless, recent advances in molecular profiling revealed distinct molecular alterations and potential therapeutic targets for BTC [3]. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) studies using whole-exome or targeted sequencing revealed a distinct genomic landscape based on the different anatomical locations of BTC. In addition, drugs targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) rearrangements and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) or IDH2 mutations have been evaluated, presenting encouraging results [4,5]. Other targetable genetic alterations including ERBB2 amplification, BRAF V600E mutations, MET alterations, or microsatellite instability are also detected in BTC. Recent National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines thus recommend the use of molecular testing to detect alterations among patients with advanced BTC [6,7]. However, the percentage of patients receiving NGS-based targeted therapy is still limited, while the majority of patients receives cytotoxic chemotherapy, with Gem/Cis being the most common scheme in daily clinical practice. Nevertheless, few studies have elucidated the predictive implications of genetic alterations in patients with advanced BTC who received cytotoxic chemotherapy. It is thus essential to determine the relevance of genetic alterations with clinical outcomes in patients treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy. In the current study, we aimed to evaluate the predictive value of specific genetic alterations on the first-line Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy and its clinical relevance in advanced BTC.
Materials and Methods1. PatientsPatients with advanced BTC, including extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), intrahepatic CCA, and gallbladder (GB) cancer from three tertiary cancer centers in South Korea were included in this study (59 patients from CHA Bundang Medical Center, 41 from Ulsan University Hospital, 93 from Severance Hospital). All patients with a targeted NGS report from a biopsy or surgical tumor specimens were retrospectively identified and data for the genomic alteration and clinicopathologic factors were collected for the integrative translational analysis. Immunohistochemical analysis for DNA mismatch repair (MMR) was performed for two MMR proteins (MLH1, MSH2) or four MMR proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2) according to the institutional guideline. Loss of MLH1/PMS2 or MSH2/MSH6 was defined as deficient MMR. The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) assay were performed with 22C3 pharm Dx assay, and interpreted with tumor proportion score (TPS) or combined positive score (CPS). PD-L1 positivity was defined as TPS ≥ 1% or CPS ≥ 1. Ampulla of Vater cancers or neuroendocrine tumors were excluded. Clinicopathologic variables including age at the beginning of treatment, sex, pathology, baseline carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9, treatment history, and survival outcome were obtained by reviewing the patients’ medical records. Among all patients, treatment outcome (responses and survival), assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) ver. 1.1, was collected and analyzed in patients who were treated with Gem/Cis-based regimen as the first-line systemic chemotherapy. The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review and Ethics Board of each institute (IRB number; CHA Bundang Medical Center: 2021-01-010, Ulsan University Hospital: 2021-01-026, Severance Hospital: 4-2020-1394). A requirement for informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective nature of the study.
2. NGS assayFormalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded blocks from diagnostic biopsy or surgical specimens were used to extract genomic DNA and RNA from NGS data. Quality assessment was performed by using quantitative polymerase chain reaction. NGS was performed in Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)-certified laboratories during clinical practice using three commercially available targeted DNA and/or RNA sequencing panels, namely Oncomine Comprehensive Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), TruSight Oncology 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA), and FoundationOne CDx (Foundation Medicine, Cambridge, MA). Variant interpretation was based on recommendations from the Association for Molecular Pathology, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the College of American Pathologists [8]. Actionable genetic alterations were stratified into one of the four levels based on OncoKB website (https://www.OncoKB.org). Tumor mutation burden (TMB) data were extracted from TruSight Oncology 500 and FoundationOne CDx assays.
3. Bioinformatics analysisPathway alteration was estimated to evaluate if there is genomic alteration on the member genes of each pathway. Gene mapping of the pathways was performed using the registered gene lists from the molecular signature database (MSigDB, https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb/). OncoKB database was used to identify mutation entities as oncogene or tumor suppressors. Mutation plots for TP53, KRAS, and ARID1A were performed using MutationMapper on cBioportal website (https://www.cbioportal.org/mutation_mapper).
4. External validation and Multi-OMICs data analysisThe dataset of genomic alteration and survival data for the external validation cohort of BTC were obtained from a public repository (https://www.cbioportal.org/). A total of 1,711 samples from 13 studies were used to externally validate the prognostic significance of BTC survival outcomes. Multi-OMICs data from the Cancer Dependency Map (DepMap) project were used to evaluate drug sensitivity according to ARID1A mutation and gene expression profiles with geneset enrichment analysis according to specific genetic mutations (https://depmap.org/portal/download).
5. Statistical analysisContinuous variables were compared using the student’s t test while categorical variables using the chi-square or Fisher exact test. Multivariate regression analysis for predictive performance of genomic alterations was performed using significant genes showing p-value less than 0.2 in univariate regression tests. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time from the initiation of first-line chemotherapy until disease progression or death (whichever comes first), while overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from the initiation of first-line chemotherapy until death. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis with visualization of survival data and the log-rank test was used to estimate statistical significance. R software (R ver. 4.1.1 for Windows) was used for statistical analysis and data visualization. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results1. Clinicopathologic characteristics of patientsA total of 193 patients with newly diagnosed advanced BTC and having NGS results from March 2016 to January 2021 were enrolled. Baseline patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. Patients were categorized according to the anatomic location of tumors in the biliary tract in terms of extrahepatic CCA (n=51), intrahepatic CCA (n=88) and GB cancer (n=54), respectively. Tumor pathology, disease extent, and baseline CA19-9 values were not statistically significant according to the anatomic location of the tumor. A total of 76 samples (39.4%) obtained from surgical specimens and 117 samples (60.6%) from biopsies were selected for targeted panel sequencing. Gem/Cis-based regimen was conducted in most patients as the first-line palliative chemotherapy (n=177, 91.7%).
2. Landscape of genomic alterationsTumor samples from 193 patients with advanced BTC were subjected to molecular profiling and the NGS reports were comprehensively reviewed. Multiple sequencing assays were used in this study, including TruSight Oncology 500 (523 target genes, Illumina) (n=84), Oncomine Comprehensive Assay version 3 (161 target genes, Thermo Fisher) (n=59), Oncomine Comprehensive Assay version 1 (143 target genes, Thermo Fisher) (n=41), and FoundationOne CDx (324 target genes, Foundation Medicine Inc.) (n=9). Several genomic alterations including single nucleotide variances and copy number alterations were identified (Fig. 1, S1 Table). TP53 was the most mutated gene in BTC (55.5%), followed by KRAS (22.8%), ARID1A (10.4%), and ERBB2 amplification (9.8%). There was a significant distinct mutation pattern based on the anatomic location of BTC. High frequency of ARID1A (19.6%) and NF1 (10.7%) alterations were observed in extrahepatic CCA, where alterations of IDH1 (11.4%), PBRM1 (8.0%), and BAP1 (8.0%) were frequently reported in intrahepatic CCA. ERBB2 amplification (16.7%), RB1 (12.5%), ARID2 alterations (8.9%), and FGFR2 amplification (7.1%) were frequent in GB cancer (Fig. 2A, S2A Fig.). Among KRAS mutations (n=44), G12D mutation (n=23, 52.3%) was the most common type in extrahepatic CCA and GB cancer, while Q61H mutation was exclusively identified in intrahepatic CCA (Fig. 2B, S2B Fig.). A significant co-occurrence of copy number alterations in the FGF family was observed, especially simultaneous FGFR2, FGF3, FGF4, CCND1, and FGF19 amplification (n=5, 2.6%) (S3 Fig.). FGFR2 fusions were reported only in two patients with intrahepatic CCA (2.3%) (Fig. 2C).
A total of seven molecular pathways including DNA damage response (76.7%), ERBB/HER signaling (52.8%), SWI/SNF complex (17.6%), Wnt/β-catenin (13.5%), fibroblast growth factor (10.9%), TGF-β signaling (10.4%), and AMPK (9.3%) pathways were revealed as frequently altered signaling pathways in BTC. A distinct pattern of pathway alteration according to the anatomic locations of BTC are presented in Fig. 2D.
3. Impact of genetic alteration on the efficacy of Gemcitabine/Cisplatin-based chemotherapyAmong the 193 patients, 177 received Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy as first-line systemic treatment. The median follow-up duration was 6.9 months (95% CI, 6.3 to 7.5). The objective response rate was 36.2% (one complete response [CR] and 63 partial response [PR] patients per RECIST ver. 1.1), and the disease control rate was 83.1%. The median PFS and OS were 7.3 months (95% CI, 6.5 to 8.1) and 24.4 months (95% CI, 17.8 to 30.9), respectively. The optimal therapy responses were correlated significantly with PFS and OS (S4 Fig.). No significant difference was reported in TMB (n=92), PD-L1 expression, MMR status, and survival outcomes based on the anatomic locations of BTC (S5 Fig.). To evaluate the impact of genetic alterations detected in the NGS with chemotherapy response to the Gem/Cis-based first-line treatment, we performed logistic regression assays to identify the predictive performance. There was no genomic alteration predicting favorable responses such as CR or PR; the pathway alterations in SWI/SNF complex containing ARID1A, negatively predicted response (CR or PR) (odds ratio [OR], 0.33; 95% CI, 0.12 to 0.75; p < 0.001) (S6 Table). Interestingly, a multivariate analysis using ARID1A, STK11, and BRCA2 alterations in all patients with BTC revealed that ARID1A alteration was the only significant predictor for primary resistance showing disease progression for 1st-line chemotherapy to Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy (OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 1.01 to 10.7; p=0.047) (Fig. 3A, S7 Table). When categorized in anatomic lesions, ARID1A alteration was significantly correlated with inferior PFS on Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy in overall patient population (p=0.002) and especially among patients with extrahepatic CCA (p=0.03) (Fig. 3B–D). In addition, STK11 alteration was related to inferior PFS in patients with intrahepatic CCA (p=0.003) (S8 Fig.). Survival analysis using Cox proportional hazard model revealed several genomic alterations showing significant impact on PFS, including ARID1A, STK11, and MRE11 in overall patients. Specifically, ARID1A, ERBB2, PBRM1, ATM, BRCA1, and RBM10 alterations were statistically significant for PFS among extrahepatic CCA, and ATM, APC, ERBB2, MRE11 alteration, and FGF19, EGFR amplification demonstrated significance in intrahepatic CCA (S9 Table, S8 Fig.). ERBB2 alteration (hazard ratio [HR], 3.4; 95% CI, 1.31 to 9.21; p=0.011), STK11 alteration (HR, 6.2; 95% CI, 1.83 to 80.92; p=0.003) and MYC amplification (HR, 78.2; 95% CI, 6.71 to 911.21; p < 0.001) was significant predictors for OS in overall patient population. SMAD4, RB1, STK, and SF3B1 alterations were associated with poor OS in intrahepatic CCA and TERT1 in GB cancer (S10 Table).
4. External validation of genetic alterationsFor the external validation of genetic alterations significance, independent clinical NGS cohorts were analyzed for BTC (13 cohorts with 1,711 patients) from public repositories. Although public data did not contain any chemotherapy efficacy data, analysis revealed that ARID1A mutation in extrahepatic or intrahepatic CCA was a significant adverse predictor for disease-free survival (extrahepatic, p=0.015; intrahepatic, p=0.066) (S11 Fig.). Survival analysis was performed for the pathway alterations, and patients with the alteration in SWI/SNF complex and ERBB2 pathway were significantly associated with poor outcomes for PFS in extrahepatic CCA (SWI/SNF, p=0.04; ERBB2, p=0.05). The alteration of TGF-beta pathway presented significantly inferior outcomes for both PFS and OS in intrahepatic CCA (PFS, p=0.02; OS, p=0.04) (S12 Fig.). In summary, ARID1A mutation not only predicted refractoriness to Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced BTC in our study cohort but was also identified as a poor prognostic factor in patients with BTC in an external validation cohort.
5. Drug sensitivity specific to ARID1A mutation using DepMap databaseIn order to comprehensively assess the drug sensitivity of cancer therapeutics according to ARID1A mutation, we obtained multi-OMICs data including genomic alteration, gene expression, and drug sensitivity data from cancer cell lines of the DepMap project data portal. In the in vitro experimental results using bile duct cancer cell lines, chemotherapeutic agents that are generally used for the treatment of BTC especially cisplatin, displayed significant drug-resistance features (Fig. 4A). Interestingly, although cisplatin is commonly used in many cancer types, our analysis showed that cisplatin-resistance caused by the ARID1A mutation was exclusively observed in bile duct cancer cells (Fig. 4B). We also discovered that two lipid-lowering drugs, namely simvastatin and mevastatin demonstrated toma significantly higher drug sensitivity compared with other cancer drugs, with simvastatin showing significant drug sensitivity according to ARID1A mutation in several cancer types including bile duct cancer (S13 Fig.).
DiscussionIn the present multicenter retrospective study, we present targeted sequencing of Korean patients with advanced BTC and identified ARID1A alteration as an adverse predictive marker for Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy. TP53 (55.5%), KRAS (22.8%), ARID1A (10.4%) mutations, and ERBB2 amplification (9.8%) were the most commonly observed genetic alterations, consistent with previous studies [9–11]. One of the major actionable mutations, the IDH-1 mutation, was reported in 11.4% of patients with intrahepatic CCA in our study cohort, which is consistent with previous studies findings [12,13]. However, FGFR2 fusion was detected in only 2.3% of patients with intrahepatic CCA in our study cohort, which was previously known to occur in 10%–16% of patients with intrahepatic CCA [14–16]. The reason for the low frequency of FGFR2 fusion may be explained using the amplicon-based approach of Oncomine panels (n=100, 51.8%), which presents a limitation in detecting fusion genes [17].
As several actionable targets such as FGFR, IDH alterations, and ERRB2 amplification have been discovered in BTC, molecular profiling has become an essential assay, recommended for the detection of actionable alterations in guidelines such as NCCN or ESMO [6]. Nevertheless, the majority of patients with advanced BTC do not present an actionable target, and these patients have limited treatment options, including first-line Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy as standard treatment since 2010. Previously, there have been efforts focusing on the discovery of new targets by conducting molecular profiling tests on BTC patients to evaluate the prognostic impact of these targets [10,18,19], but none of these studies evaluated the predictive value of specific genetic alterations to systemic chemotherapy using NGS. In the current study, we identified, for the first time, the genetic alteration predicting the therapeutic efficacy of systemic chemotherapy by correlating the genetic alterations identified in multicenter large-scale NGS analyses, with the survival outcomes of BTC patients treated with first-line Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy.
ARID1A, AT-Rich interaction domain 1A, is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling SWI/SNF complex required for the transcriptional activation of specific genes that are normally repressed by chromatin. Loss of ARID1A expression, either by inactivation of mutations or epigenetic silencing, contributes to carcinogenesis via aberrant epigenetic regulations of gene expression, cell cycle deregulation, or defective DNA repair [20]. ARID1A alterations have been commonly detected to be mutated among many cancer types including gastric cancers [21], ovarian cancers [22], and pancreatic cancers [23]. As ARID1A functions as a tumor suppressor, negative expression or loss of function mutations of ARID1A have been related to worse survival outcome among various cancers [24,25], although correlation of its predictive role with the treatment regimen has not been previously reported. In the current study, approximately 10% of patients with BTC presented alterations of ARID1A, which were all loss of function mutations. ARID1A alteration has been investigated in depth in BTC with respect to its prognostic role, however, the results were controversial [9,26–28]. Previous studies examining the role of ARID1A alterations in BTC were primarily performed in patients with surgical resection or heterogeneous population, which makes the assessment of its prognostic significance challenging. We suggested alteration of ARID1A as a predictive NGS-based biomarker that predicts poor response and survival for patients with advanced BTC treated with first-line Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy, which has never been reported before. The results of this study were supported by drug sensitivity data analyses from cancer cell lines of a public database suggesting that BTC cell lines with ARID1A mutations also demonstrated resistance to cisplatin. Interestingly, this was not observed in other cancer cells with ARID1A mutations. Nevertheless, further mechanistic studies to reveal this unique cisplatin-resistance feature of ARID1A-altered BTC are required.
ARID1A is not currently an actionable target, as there are no gene-specific treatment options for poor prognostic ARID1A-altered BTC. Nevertheless, another interesting discovery from cancer cell lines analysis of drug sensitivity data was that ARID1A-altered BTC cell lines were responsive to statins. A previous study supports that statins may reduce mitochondrial electron carrier coenzyme Q in cancer cells [29], apart from inhibiting the mevalonate pathway. As recent preclinical studies demonstrated that inactivation of ARID1A lead to metabolic vulnerability in cancer cells that requires glutamine utilization via glutaminase1 upregulation [30], statins may act through a mechanism of synthetic lethality to ARID1A-altered BTC by inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation. Further validation containing functional and clinical studies are however required.
One of the limitations of the current study was that different targeted panel sequencing platforms were used for genetic analysis. Due to differences in gene coverages or extent of capture regions across NGS platforms, information on fusion genes and TMB was not available in all cases. Furthermore, genetic analyses were primarily conducted at the DNA level, and RNA sequencing was only employed to discover the presence of fusions, the functional consequences of these genetic alterations requires thus further investigation. Additionally, the presented study was performed retrospectively. Despite these limitations, this study is crucial, as it presented predictive biomarkers from a large homogeneous population of BTC patients treated with Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy, which is pivotal treatment for patients with advanced BTC for more than decade. Moreover, a relatively large number of extrahepatic CCA cases which are difficult to obtain tumor tissues were included in the study.
In conclusion, integrative analysis with genomic alterations and survival outcomes in advanced BTC revealed that patients with ARID1A mutations are associated with primary resistance to Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy, especially in patients with extrahepatic CCA. Consequently, in patients with BTC with ARID1A mutation, thorough assessment of the treatment response needs to be incorporated in clinical practice to minimize adverse outcomes after Gem/Cis-based chemotherapy. Well-designed prospective studies are mandatory to validate the predictive role of ARID1A mutation.
Electronic Supplementary MaterialSupplementary materials are available at Cancer Research and Treatment website (https://www.e-crt.org).
NotesEthical Statement This study was approved by the Institutional Review and Ethics Board of each institute (IRB number; CHA Bundang Medical Center: 2021-01-010, Ulsan University Hospital: 2021-01-026, Severance hospital: 4-2020-1394) and was performed in accordance with the ethics of the institutional research committee and the recent Declaration of Helsinki. A requirement for informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective nature of the study. Author Contributions Conceived and designed the analysis: Cheon J, Lee CK, Chon HJ. Collected the data: Lee SH, Cheon J, Lee S, Kang B, Kim C, Choi SH, Choi HJ, Lee CK, Chon HJ. Contributed data or analysis tools: Lee SH, Cheon J, Lee S, Shim HS, Park YN, Jung S, Choi SH, Choi HJ, Lee CK, Chon HJ. Performed the analysis: Lee SH, Cheon J, Lee S, Kang B, Kim C, Shim HS, Park YN, Jung S, Choi SH, Choi HJ, Lee CK, Chon HJ. Wrote the paper: Lee SH, Cheon J, Lee CK, Chon HJ. Conflicts of Interest H.J.C received research grants from Roche; consulting or advisory role at Roche, Celgene, Bayer, Eisai, ONO pharmaceuticals, BMS, Sanofi, Servier, and MSD. J.C received research grants from Bayer; consulting or advisory role at Roche and Eisai. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. AcknowledgmentsWe would like to thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for English language editing.
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government (NRF-NRF-2020R1C1C1010722 to H.J.C.; NRF-2020R1C1C1004461 to C.-k.L).
Fig. 1Genomic alteration associated with anatomic locations of biliary tract cancer. Oncoplot showing non-silent mutation counts for individual tumors (top), frequently mutated top 40 genes (middle), and other clinical factors including center, sex, age, sequencing panel, and MMR status (bottom). CCA, cholangiocarcinoma; dMMR, deficient mismatch repair; EHC, extrahepatic cholangiocarcinomar; GB, gallbladder cancer; MMR, mismatch repair; MSI, microsatellite instability; MSS, microsatellite stable; NGS, next generation sequencing. 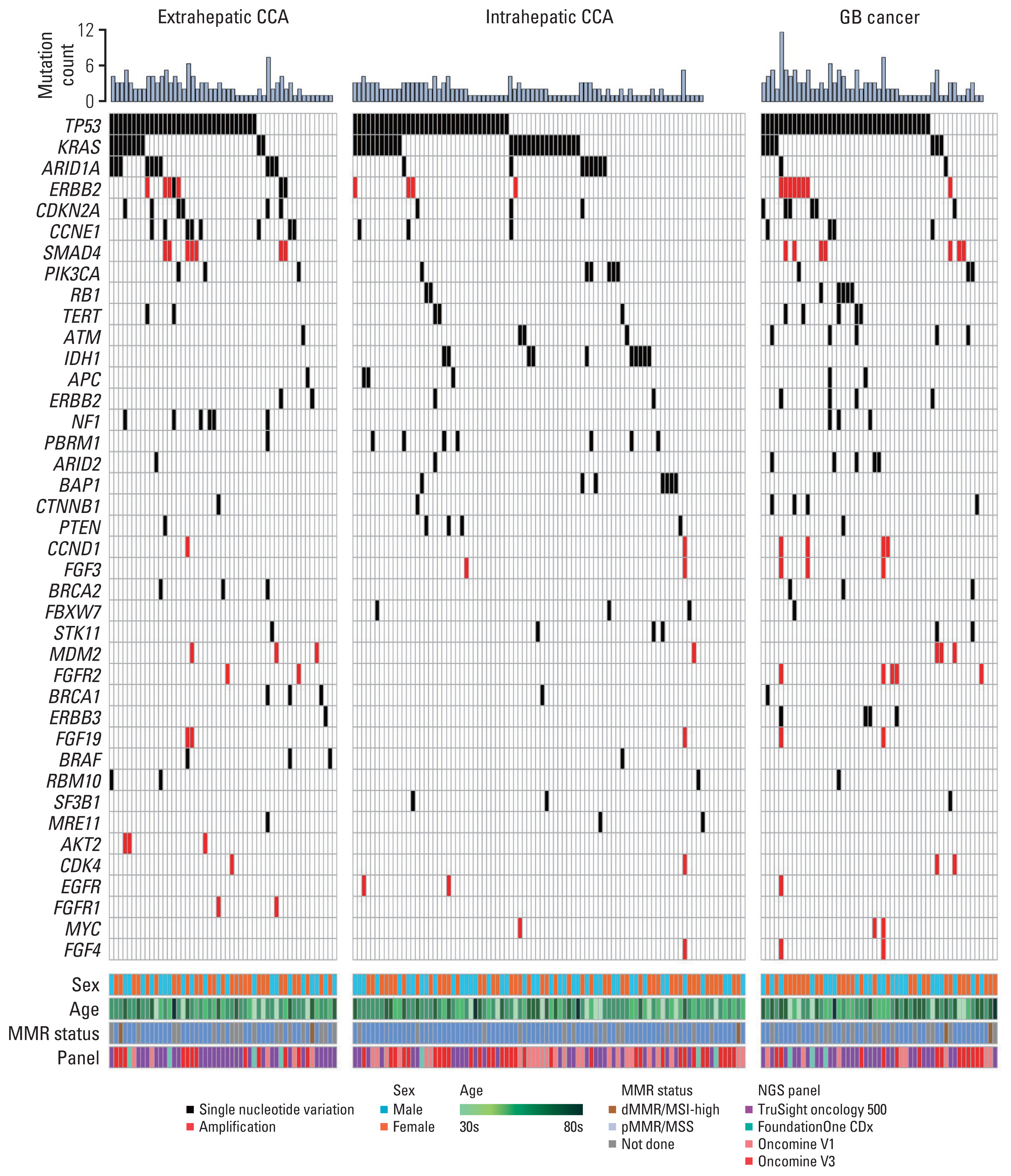
Fig. 2Alteration pattern associated with anatomic locations of biliary tract cancer. (A) Bar plot showing the relative fraction of alterations for ERBB2 amplification and IDH1. p-value was calculated using the chi-square test. (B) Stacked bap plot for single nucleotide changes for KRAS according to the anatomic location. (C) Circos plot representing fusion events. Red color indicates extrahepatic while green color indicates intrahepatic location. (D) Diagram for pathway alteration presenting the percentage of samples for each anatomic location with respect to DNA damage response, ErbB/HER signaling, Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β signaling, fibroblast growth factor and AMPK pathways, as well as the SWI/SNF complex, respectively. CCA, cholangiocarcinoma; GB, gallbladder cancer. 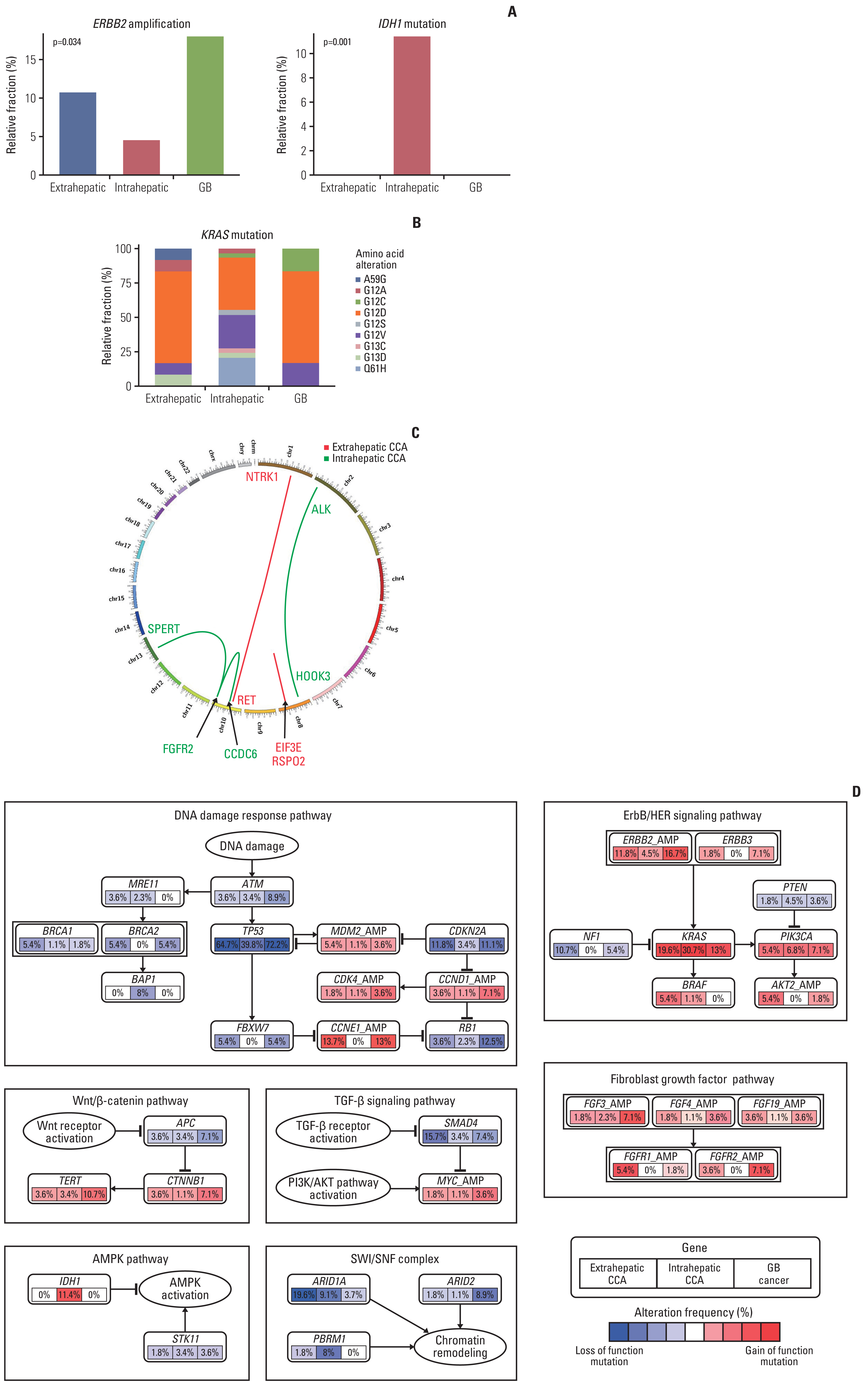
Fig. 3Prediction of clinical outcomes according to prognostic genes. (A) Forest plot showing significant genes, for predicting disease progression (ARID1A, BRCA2, and STK11) after first-line chemotherapy from multivariate logistic regression. (B) Kaplan-Meier plot demonstrating survival difference for progression-free survival according to ARID1A in total biliary tract cancer patients. (C) Stacked bar plot indicating optimal response after first-line chemotherapy according to ARID1A mutation in EHC. (D) Kaplan-Meier plot presenting survival difference for progression-free survival according to ARID1A in EHC. p-value was estimated using the log-rank test. CCA, cholangiocarcinoma; CI, confidence interval; EHC, extrahepatic cholangiocarcinomar; OR, odds ratio; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease. 
Fig. 4Drug sensitivity of cancer cells according to ARID1A mutation. (A) Volcano plot presenting sensitive or resistant drugs according to ARID1A mutation. p-value was estimated using the student’s t test. (B) Grouped bar plot showing ARID1A-specific drug sensitivity for cisplatin according to cancer types. p-value was calculated using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; NA, not available. 
Table 1Baseline patient characteristics
References1. Bridgewater JA, Goodman KA, Kalyan A, Mulcahy MF. Biliary tract cancer: epidemiology, radiotherapy, and molecular profiling. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016;35:e194–203.
2. Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D, Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1273–81.
3. Valle JW, Lamarca A, Goyal L, Barriuso J, Zhu AX. New horizons for precision medicine in biliary tract cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:943–62.
4. Abou-Alfa GK, Sahai V, Hollebecque A, Vaccaro G, Melisi D, Al-Rajabi R, et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:671–84.
5. Zhu AX, Macarulla T, Javle MM, Kelley RK, Lubner SJ, Adeva J, et al. Final overall survival efficacy results of ivosidenib for patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma with IDH1 mutation: the phase 3 randomized clinical ClarIDHy trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1669–77.
6. Mosele F, Remon J, Mateo J, Westphalen CB, Barlesi F, Lolkema MP, et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: a report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1491–505.
7. Benson AB, D’Angelica MI, Abbott DE, Anaya DA, Anders R, Are C, et al. Hepatobiliary cancers, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:541–65.
8. Li MM, Datto M, Duncavage EJ, Kulkarni S, Lindeman NI, Roy S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation and reporting of sequence variants in cancer: a joint consensus recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J Mol Diagn. 2017;19:4–23.
9. Lowery MA, Ptashkin R, Jordan E, Berger MF, Zehir A, Capanu M, et al. Comprehensive molecular profiling of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas: potential targets for intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4154–61.
10. Chae H, Kim D, Yoo C, Kim KP, Jeong JH, Chang HM, et al. Therapeutic relevance of targeted sequencing in management of patients with advanced biliary tract cancer: DNA damage repair gene mutations as a predictive biomarker. Eur J Cancer. 2019;120:31–9.
11. Nakamura H, Arai Y, Totoki Y, Shirota T, Elzawahry A, Kato M, et al. Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1003–10.
12. Boscoe AN, Rolland C, Kelley RK. Frequency and prognostic significance of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutations in cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic literature review. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019;10:751–65.
13. Zhu AX, Borger DR, Kim Y, Cosgrove D, Ejaz A, Alexandrescu S, et al. Genomic profiling of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: refining prognosis and identifying therapeutic targets. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:3827–34.
14. Graham RP, Barr Fritcher EG, Pestova E, Schulz J, Sitailo LA, Vasmatzis G, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 translocations in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2014;45:1630–8.
15. Ross JS, Wang K, Gay L, Al-Rohil R, Rand JV, Jones DM, et al. New routes to targeted therapy of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas revealed by next-generation sequencing. Oncologist. 2014;19:235–42.
16. Farshidfar F, Zheng S, Gingras MC, Newton Y, Shih J, Robertson AG, et al. Integrative genomic analysis of cholangiocarcinoma identifies distinct IDH-mutant molecular profiles. Cell Rep. 2017;19:2878–80.
17. Bruno R, Fontanini G. Next generation sequencing for gene fusion analysis in lung cancer: a literature review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10:521.
18. Yoon JG, Kim MH, Jang M, Kim H, Hwang HK, Kang CM, et al. Molecular characterization of biliary tract cancer predicts chemotherapy and programmed death 1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade responses. Hepatology. 2021;74:1914–31.
19. Montal R, Sia D, Montironi C, Leow WQ, Esteban-Fabro R, Pinyol R, et al. Molecular classification and therapeutic targets in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2020;73:315–27.
20. Pavlidou EN, Balis V. Diagnostic significance and prognostic role of the ARID1A gene in cancer outcomes (review). World Acad Sci J. 2020;2:49–64.
21. Wang K, Kan J, Yuen ST, Shi ST, Chu KM, Law S, et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of ARID1A in molecular subtypes of gastric cancer. Nat Genet. 2011;43:1219–23.
22. Wiegand KC, Shah SP, Al-Agha OM, Zhao Y, Tse K, Zeng T, et al. ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1532–43.
23. Shain AH, Giacomini CP, Matsukuma K, Karikari CA, Bashyam MD, Hidalgo M, et al. Convergent structural alterations define SWItch/Sucrose NonFermentable (SWI/SNF) chromatin remodeler as a central tumor suppressive complex in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E252–9.
24. Luchini C, Veronese N, Solmi M, Cho H, Kim JH, Chou A, et al. Prognostic role and implications of mutation status of tumor suppressor gene ARID1A in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:39088–97.
25. Berns K, Sonnenblick A, Gennissen A, Brohee S, Hijmans EM, Evers B, et al. Loss of ARID1A activates ANXA1, which serves as a predictive biomarker for trastuzumab resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:5238–48.
26. Javle M, Bekaii-Saab T, Jain A, Wang Y, Kelley RK, Wang K, et al. Biliary cancer: Utility of next-generation sequencing for clinical management. Cancer. 2016;122:3838–47.
27. Conci S, Ruzzenente A, Simbolo M, Bagante F, Rusev B, Isa G, et al. Multigene mutational profiling of biliary tract cancer is related to the pattern of recurrence in surgically resected patients. Updates Surg. 2020;72:119–28.
28. Xu SF, Guo Y, Zhang X, Zhu XD, Fan N, Zhang ZL, et al. Somatic mutation profiling of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: comparison between primary and metastasis tumor tissues. J Oncol. 2020;2020:5675020.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||