AbstractPurposeThe expression of the PIM-1 gene, which is a proto-oncogene that encodes a serine/threonine kinase, is associated with multiple cellular functions such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and tumorigenesis. In particular, several studies have reported that the PIM-1 gene is associated with the development of lymphoma, leukemia and prostate cancer. Therefore, this study was conducted to evaluate the association between the single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PIM-1 gene and the risk of lung cancer occurrence in the Korean population.
Materials and MethodsTo evaluate the role of the PIM-1 gene in the development of lung cancer, the genotypes of the PIM-1 gene were determined in 408 lung cancer patients and 410 normal subjects.
ResultsWe found that the T-C-T-C haplotypes of the PIM-1 gene (-1196 T>C, IVS4 +55 T>C, IVS4 +1416 T>A and +3684 C>A) were associated with an increased risk of lung cancer [adjusted odds ratio (aOR): 3.98; 95% CI: 1.24~12.75, p-value: 0.020]. In particular, these haplotypes showed an increased risk of lung cancer in males (aOR: 5.67; 95% CI: 1.32~24.30, p-value: 0.019) and smokers (aOR: 7.82; 95% CI: 1.75~34.98, p-value: 0.007).
INTRODUCTIONThere have been numerous previous researches and reports about proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes and their roles in the development of cancer. PIM-1 gene is a proto-oncogene that encodes a serine/threonine kinase, which belongs to the group of calcium/calmodulin-regulated kinases, and this PIM-1 kinase controls such cellular functions as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and tumorigenesis through various signaling pathways. It has been verified that the PIM-1 gene is related with several human cancers, including lymphoma, leukemia and prostate cancer (1-3). However, the relationship between the PIM-1 gene and lung cancer has not yet been reported.
It is well known that various signaling pathways are related with the development of lung cancer. Several tyrosine kinase inhibitors and serine/threonine kinase inhibitors that block serine/threonine signaling pathways have been introduced as anti-neoplastic agents against lung cancer (4,5). Therefore, we attempted to characterize the association between the polymorphisms of the PIM-1 gene that encodes serine/threonin kinase and the risk of developing lung cancer in a Korean population by using genotype and haplotype analysis.
Lung cancer has been the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in Korea, and its incidence continues to rise (6). Nevertheless, the prognosis of lung cancer has remained poor despite the innovations in diagnostic testing and surgical technique, and the development of new chemotherapeutic agents (7). The poor outcomes of lung cancer may partly be due to the heterogeneity of lung cancer histobiology (8) because different histological subtypes have distinctive etiologies and different responses to anticancer therapy, and these subtypes should be treated differently. Moreover, the recently introduced targeted agents show different responses according to the histologic subtype (5), and the efficiency of the treatment modalities for lung cancer depends on the time of diagnosis. Thus, there is a great need for rapid and efficient methods to detect lung cancer at an early stage. For developing improved molecular biomarkers for early detection and to predict the response to chemotherapy, it is important to identify the genetic alterations that are specific to each subtype of lung cancer.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most abundant form of genetic variation in the human genome, and these occur when a single nucleotide in the genome sequence is altered (9). Theoretically, the numbers of SNPs in human population have been estimated to be about 5 million SNPs for minor allele frequencies of at least 10%, and possibly as many as 11 million for minor allele frequencies of at least 1% (10). SNPs have an excellent potential to be used as biomarkers for diagnosing genetic diseases, including cancers, as compared to other less common polymorphisms and microsatellite markers.
This study was conducted to examine the PIM-1 polymorphisms and their relation with the risk of lung cancer in a Korean population. To the best of our best knowledge, this is the first study to determine an association of the PIM-1 polymorphisms with lung cancer in Korean lung cancer patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS1) The study subjectsBetween August 2001 and June 2007, blood samples were collected from 818 subjects, and these included 408 lung cancer patients and 410 normal controls without cancer. The lung cancer patients were recruited from the patient pool at the Genomic Research Center for Lung and Breast/Ovarian Cancer and the Inha University Medical Center, and the control subjects were randomly selected from a pool of healthy volunteers who had visited the Cardiovascular Genome Center, the Genomic Research Center for Allergy and Respiratory Diseases and Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center. Detailed information on the subjects' diet, their smoking status, drinking status, lifestyle and medical history were collected by trained interviewers with using a structured questionnaire. Out of the 408 cases, 397 smoking statuses, 311 drinking statuses, 313 stages and 385 cell types were available for the characteristic information, while 309 smoking statuses and 211 drinking statuses for the 410 controls were available for the characteristic information. All the study subjects provided written consent and they were all ethnic Koreans, and all the participating Institutional Review Boards approved the study protocol.
2) Preparation of genomic DNA and direct sequencingGenomic DNA was prepared from peripheral blood samples with using a Puregene blood DNA kit (Gentra, Minneapolis, MN) and following the manufacture's protocol. For identification of the frequent polymorphism sites in the PIM-1 gene in the Korean population, human genomic DNA was isolated for direct sequencing from the whole blood of 24 samples. We amplified the entire PIM-1 gene at 6p21, and PCR amplifications were performed on a PTC-225 Peltier Thermal cycler (MJ Research Inc., Waltham, MA) with using AmpliTagGold (Roche, Branchburg, NJ); there were 35 cycles of 30 s at 95℃, 1 min at 64℃ and 1 min at 72℃, followed by a single 10 min extension step at 72℃. The PCR products were purified using a Montage PCR96 Cleanup kit (Millipore, Bedfore, MA) and they were eluted with 20 µl of nuclease free H2O. DNA cycle sequencing was carried out using a BigDye Terminator V 3.1 Cycle Sequencing kit (PerkinElmer, Foster City, CA). Multiscreen SEQ 384 well filter plates were used for dye terminator removal, and the sequences were analyzed on an Applied Biosystems 3,700 DNA analyzer. All the SNPs and sequence alignments were analyzed with using Polyphred.
3) GenotypingAfter direct sequencing of the PIM-1 gene, we performed genotyping for the SNPs with a frequency greater than 5%. The genotypes of the sample were assayed using a single base primer extension assay and using a SNaPShot assay kit (ABI, Foster City, CA). Briefly, the genomic regions containing the SNPs of interest in the PIM-1 gene were amplified by PCR. PCRs were performed using an initial denaturation step at 95℃ for 10 min and 35 amplification cycles (30 s at 95℃, 1 min annealing at 63.9℃ and 1 min at 72℃), followed by a single 7 min extension cycle at 72℃. The PCR products were subsequently purified by incubating them with 10 units of ExoI (USB, Cleveland, OH) and 1 unit of shrimp alkaline phosphatase (Roche, Indianapolis, IN) at 37℃ for 1 h and at 72℃ for 15 min. Extension reactions with 1 µl of purified PCR product, 0.15 pmol of genotyping primer and a SNaPshot Multiplex Ready Reaction Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) were carried out by repeating the following cycle 25 times: 96℃ for 10 s, 50℃ for 5 s and 60℃ for 30 s. The extension products were incubated with 1 unit of shrimp alkaline phosphatase (Roche, Indianapolis, IN) at 37℃ for 1 h and next at 72℃ for 15 min. Nine microliters of deionized formamide was mixed with 1 µl of the purified extension product, and the mixture was electrophoresed on an ABI Prism 3,700 genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The results were analyzed using GeneScan analysis, version 3.7 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).
4) Statistical analysisThe allele frequencies and genotype frequencies and the departures of the genotype distributions from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for each SNP were analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was tested on pairwise combinations of SNPs with using the absolute value of the standardized measure of linkage disequilibrium, D', as calculated by the Haploview program version 3.2 (11). The haplotypes and their frequencies were estimated by the Haploview program version 3.2. The genotype-specific risks were estimated as odds ratios (ORs) with associated 95% confidence intervals by unconditional logistic regression (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) and these were adjusted for age, gender and the smoking status.
RESULTSA total of 818 patients were enrolled in the study. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the study subjects. The baseline characteristics were similar between the case group and control group; however, there were significant differences in the smoking status between groups. By direct sequencing of the PIM-1 gene, we discovered 15 polymorphisms among the 24 samples from lung cancer patients. We focused on 4 SNPs in the PIM-1 gene (-1196 T>C, IVS4 +55 T>C, IVS4 +1416 T>A and +3684 C>A), which showed more than 5% minor allele frequencies of 0.072, 0.285, 0.139 and 0.139, respectively. Fig. 1 shows the structure of the PIM-1 gene and the linkage disequilibrium. The genotype frequencies of these SNPs in the patients and controls were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
The associations between the risk of lung cancer in Koreans and the polymorphisms of the PIM-1 gene and the haplotypes were analyzed. The genotype distributions for the cancer and control groups and the estimated associations with the lung cancer risk, as stratified by gender and the smoking status, are shown in Table 2. No significant difference was found in the distributions of the genotypes for all the tested polymorphisms between the overall lung cancer cases and the controls. However, the subsequent haplotype analysis revealed that the T-C-T-C haplotype was associated with susceptibility to the risk of lung cancer (aOR: 3.98; 95% CI: 1.24~12.75, p-value: 0.020), according to the multiple logistic regression analysis (Table 3). The T-C-T-C haplotype was more significantly associated with the increased risk for lung cancer in males (aOR: 5.67; 95% CI: 1.32~24.30, p-value: 0.019) and smokers (aOR: 7.82; 95% CI: 1.75~34.98, p-value: 0.007).
DISCUSSIONIn this study on 818 Korean lung cancer patients and controls, we found that four single nucleotide polymorphisms (-1196 T>C, IVS4 +55 T>C, IVS4 +1416 T>A and +3684 C>A) in the PIM-1 gene were not significantly associated with an increased risk for lung cancer. However, the haplotype analysis showed that the T-C-T-C haplotype was significantly associated with an increased risk for lung cancer, and especially in males (aOR: 5.67; 95% CI: 1.32~24.30, p-value: 0.019) and smokers (aOR: 7.82; 95% CI: 1.75~34.98, p-value: 0.007). Although smoking itself plays a critical role in the development of lung cancer (12), only a fraction of smokers develop lung cancer. The reason for this discrepancy in the smoking population has not been clearly delineated. Nevertheless, it is highly possible that smoking plays an additional role to the genetic alterations in lung cancer patients. Although there has been no direct evidence to show that smoking induces DNA methylation, several studies have suggested that DNA hypermethylation is associated with exposure to cigarette smoking (13,14). The studies on RASSF1A, which is a tumor suppression gene, indicated that the loss of heterozygosity and epigenetic inactivation of the RASSF1A promoter lead to down-regulation of gene expression, and this subsequently increases the risk of lung cancer (15). This suggests that the genetic constitution of individuals is of importance in determining the susceptibility of individuals to lung cancer (16). In our previous study on the RASSF1A promoter, similar results were also obtained for the smoking status (17). In the present study, we obtained further evidence to indicate that polymorphisms of the PIM-1 proto-oncogene increased the susceptibility of lung carcinogenesis due to smoking. However, an additional functional study of PIM-1 kinase is needed regarding this subject.
Since the PIM-1 gene was first recognized 20 years ago as a proviral insertion site of the Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV), many serial studies have established the PIM-1 gene as a proto-oncogene and an important player in the process of malignant transformation (18,19). The overexpression and mutation of PIM-1 kinase have been reported in various tumors of animal models, as well as in human tumors (18,19). The PIM family is composed of three highly homologous genes, PIM-1, PIM-2 and PIM-3, and they are well conserved in vertebrates and they show high degrees of sequence and structural similarities (20). In animal models, PIM-1 protein kinases have been shown to enhance the development of lymphoma, acute leukemia and prostate cancer (21). PIM-2 overexpression is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (22), whereas PIM-3 shows an aberrant expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (23). In humans, the protein levels of PIM-1 have been shown to be elevated in lymphomas, leukemias and prostate cancer (1-3). Especially, the PIM-1 gene has the potential to be a diagnostic and prognostic marker for prostate cancer because microarray analysis (RT-PCR or immunohistochemical analysis) has revealed that the PIM-1 gene was differentially expressed between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer (3).
The tumor suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes of lung cancer have been extensively studied, and this has revealed new information about their polymorphisms and hypermethylation (17,24,25). However, there has been no study on the role of the PIM-1 gene in the development of lung cancer. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to address this issue. In the present study, we report on 4 SNPs of the PIM-1 gene, and these SNPs were found for the first time in a Korean population. The polymorphism of -1196 T>C was the novel SNP, and the polymorphism of IVS4 +55 T>C was already known, but the frequencies of these SNPs have not been reported in the world's medical literature. The other 2 SNPs had not been reported in the Korean population. The observed frequencies of the minor alleles of IVS4 +1416 T>A and +3684 C>A in our study were 0.139 and 0.139, respectively. In the dbSNP database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP), the Asian ethnic group's frequency of the minor allele of IVS4 +1416 T>A had been reported to be 0.628 (Han Chinese) and 0.489 (Japanese), but the frequency of the minor allele of +3684 C>A has not been previously reported for an Asian ethnic group.
The limitation of this study was the small size of the (-/-) haplotype pair group in the ht2 T-C-T-C haplotype, and this small size could lead to random error. However, we thought the results had significance because the above results were adjusted according to multiple variables and the results were derived from a relatively large-sized sample group.
CONCLUSIONThis is the first study to identify the association between the PIM-1 gene polymorphisms and the risk of lung cancer. In this study, we found that the T-C-T-C haplotype of the PIM-1 gene (-1196 T>C, IVS4 +55 T>C, IVS4 +1416 T>A and +3684 C>A) could influence the risk of developing smoking-related lung cancer in the Korean population. Additional functional studies with larger sized study populations are needed in the future to reconfirm our findings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTSWe thank Young Lim, Dong-Hoon Shin, Choon-Sik Park and Yangsoo Jang for the sample collection and provision.
NotesThis study was supported by a grant of the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A010250). References1. Ionov Y, Le X, Tunquist BJ, Sweetenham J, Sachs T, Ryder J, et al. PIM-1 protein kinase is nuclear in Burkitt's lymphoma: nuclear localization is necessary for its biologic effects. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:167–178. PMID: 12680209
2. Pasqualucci L, Neumeister P, Goossens T, Nanjangud G, Chaganti RS, Kuppers R, et al. Hypermutation of multiple proto-oncogenes in B-cell diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Nature. 2001;412:341–346. PMID: 11460166
3. Xu Y, Zhang T, Tang H, Zhang S, Liu M, Ren D, et al. Overexpression of PIM-1 is a potential biomarker in prostate carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2005;92:326–330. PMID: 16299799
4. Oh Y, Herbst RS, Burris H, Cleverly A, Musib L, Lahn M, et al. Enzastaurin, an oral serine/threonine kinase inhibitor, as second- or third-line therapy of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1135–1141. PMID: 18309949
5. Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. PMID: 16014882
6. Shin HR, Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Yim SH, Sung JH, et al. National Cancer Incidence for the Year 2002 in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2007;39:139–149.
7. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. PMID: 15761078
8. Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y. The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 2001;18:1059–1068. PMID: 11829087
9. Matsuzaki H, Loi H, Dong S, Tsai YY, Fang J, Law J, et al. Parallel genotyping of over 10,000 SNPs using a one-primer assay on a high-density oligonucleotide array. Genome Res. 2004;14:414–425. PMID: 14993208
10. Kruglyak L, Nickerson DA. Variation is the spice of life. Nat Genet. 2001;27:234–236. PMID: 11242096
11. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263–265. PMID: 15297300
12. Khuder SA. Effect of cigarette smoking on major histological types of lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2001;31:139–148. PMID: 11165392
13. Belinsky SA, Palmisano WA, Gilliland FD, Crooks LA, Divine KK, Winters SA, et al. Aberrant promoter methylation in bronchial epithelium and sputum from current and former smokers. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2370–2377. PMID: 11956099
14. Kim DH, Kim JS, Ji YI, Shim YM, Kim H, Han J, et al. Hypermethylation of RASSF1A promoter is associated with the age at starting smoking and a poor prognosis in primary non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3743–3746. PMID: 12839968
15. Agathanggelou A, Honorio S, Macartney DP, Martinez A, Dallol A, Rader J, et al. Methylation associated inactivation of RASSF1A from region 3p21.3 in lung, breast and ovarian tumours. Oncogene. 2001;20:1509–1518. PMID: 11313894
16. Shields PG, Harris CC. Cancer risk and low-penetrance susceptibility genes in gene-environment interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2309–2315. PMID: 10829052
17. Sung JS, Han SG, Whang YM, Shin ES, Lee JW, Lee HJ, et al. Putative association of the single nucleotide polymorphisms in RASSF1A promoter with Korean lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2008;61:301–308. PMID: 18313166
18. Bachmann M, Moroy T. The serine/threonine kinase PIM-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:726–730. PMID: 15694833
19. Wang Z, Bhattacharya N, Weaver M, Petersen K, Meyer M, Gapter L, et al. PIM-1: a serine/threonine kinase with a role in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Vet Sci. 2001;2:167–179. PMID: 12441685
20. Mikkers H, Nawijn M, Allen J, Brouwers C, Verhoeven E, Jonkers J, et al. Mice deficient for all PIM kinases display reduced body size and impaired responses to hematopoietic growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:6104–6115. PMID: 15199164
21. Cuypers HT, Selten G, Quint W, Zijlstra M, Maandag ER, Boelens W, et al. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984;37:141–150. PMID: 6327049
22. Cohen AM, Grinblat B, Bessler H, Kristt D, Kremer A, Schwartz A, et al. Increased expression of the hPim-2 gene in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004;45:951–955. PMID: 15291354
23. Fujii C, Nakamoto Y, Lu P, Tsuneyama K, Popivanova BK, Kaneko S, et al. Aberrant expression of serine/threonine kinase Pim-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma development and its role in the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 2005;114:209–218. PMID: 15540201
24. Herman JG, Baylin SB. Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2042–2054. PMID: 14627790
25. Thomas RK, Weir B, Meyerson M. Genomic approaches to lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4384s–4391s. PMID: 16857815
Fig. 1Gene map and haplotypes of the PIM-1 gene. Coding exons are marked by the black blocks and the 5' and 3' UTR are marked by the white blocks. The first base of the translational site was denoted as nucleotide +1 (A). The LD blocks organization of the PIM-1 gene (B). Haplotypes of the PIM-1 gene (C). 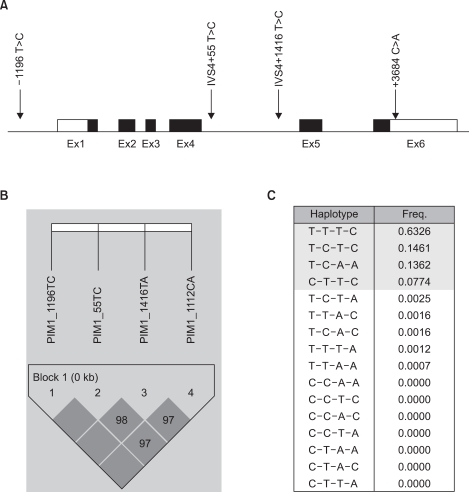
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||